After cancelling nearly $7.6B in clean energy funding, dozens of climate projects — and community benefits — may be at risk.

The Trump administration has announced plans to cancel about $7.6 billion in federal funding across more than 200 clean energy and climate-related projects, many of them in Democratic-leaning states. The cuts target initiatives such as hydrogen hubs, battery plants, grid modernization efforts, and carbon capture projects, including a $1.2 billion award for California’s hydrogen program. Officials argue the programs did not adequately advance national energy needs or provide sufficient taxpayer returns, but critics warn the move could harm jobs, innovation, and local economies.
1. Billions in Climate Funding Suddenly Cut

The administration cancelled about $7.6 billion in federal support across more than 200 projects. These programs were designed to accelerate the shift to clean energy, improve power grids, and lower emissions nationwide.
The decision marks one of the largest reversals of climate funding in recent history. While officials argue the cuts are necessary to protect taxpayer dollars, critics say they will disrupt years of planning and stall projects already in development, leaving communities uncertain about their energy future.
2. California’s Hydrogen Hub Loses $1.2 Billion

One of the largest cancelled awards was a $1.2 billion commitment to California’s hydrogen hub project. This initiative aimed to expand hydrogen fuel as a clean alternative for transportation and heavy industry.
State officials warn that without federal backing, the program may struggle to move forward at scale. Supporters argue that California’s hub could have become a national model for lowering emissions, while the loss of funding now risks slowing momentum in one of the country’s most ambitious climate programs.
3. Hydrogen Projects Across States Face Setbacks

Beyond California, multiple hydrogen projects across the U.S. were hit by the funding cuts. These projects were part of a broader effort to develop regional hydrogen networks that could provide clean energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
The cancellations raise questions about whether private investment will be enough to keep these initiatives alive. Experts warn that pulling federal support could discourage innovation, delay job creation, and allow other countries to surpass the U.S. in the race to build a competitive hydrogen economy.
4. Battery Manufacturing Investments Pulled Back

Several projects focused on advancing battery technology also lost their funding. These included facilities meant to produce advanced batteries for electric vehicles and grid storage, both crucial for lowering emissions.
The loss of support comes as global demand for batteries is surging. Critics argue that cutting U.S. investment now could make the country more dependent on overseas suppliers, especially in China, which already dominates the battery market. That dependence may leave America vulnerable in both energy security and economic competitiveness.
5. Grid Modernization Projects Halted
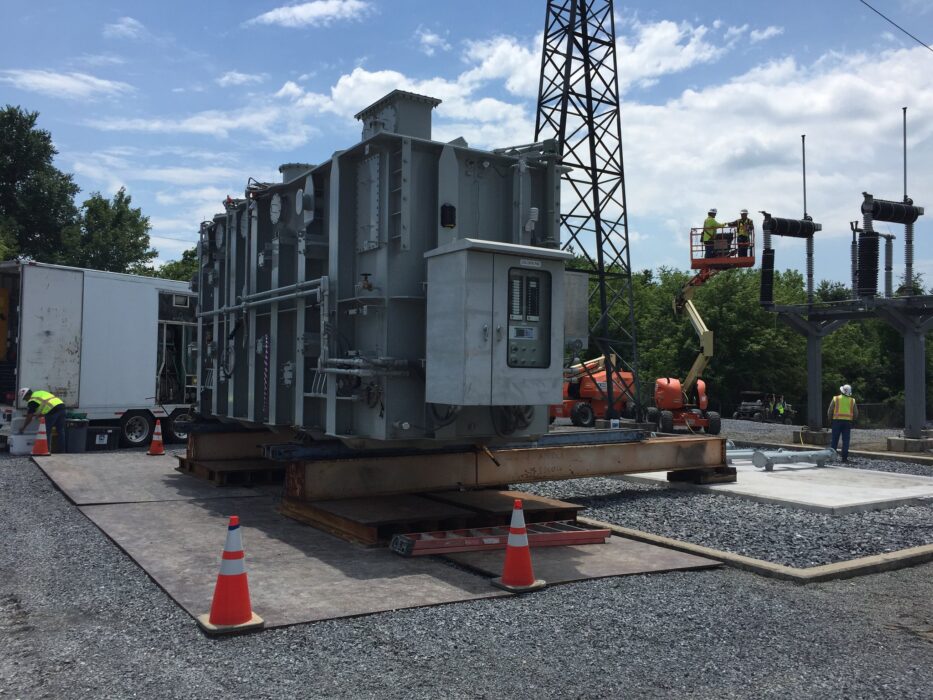

The cuts also targeted programs meant to upgrade and modernize power grids across the country. These efforts aimed to make grids more resilient against extreme weather, improve efficiency, and integrate renewable energy.
Without these upgrades, experts warn that parts of the grid will remain outdated and vulnerable. Communities could face more frequent blackouts, higher costs, and greater challenges connecting new clean energy sources. The cancellations may also make it harder to prepare for the impacts of climate-driven heat waves, storms, and fires.
6. Carbon Capture Programs Cancelled

Some of the cancelled projects included research and pilot plants for carbon capture and storage. These programs were intended to test whether emissions from industrial facilities and power plants could be captured before reaching the atmosphere.
Carbon capture has been controversial, with critics saying it is expensive and unproven at scale. Still, losing billions in potential investment means fewer opportunities to refine the technology. This could delay efforts to meet emissions goals and reduce options for industries that struggle to transition away from fossil fuels.
7. Economic Fallout for Local Communities

Many of the cancelled projects were expected to bring jobs and economic development to the regions where they were based. Construction of new facilities, training programs, and long-term operations could have supported thousands of workers.
With funding now withdrawn, communities face uncertainty about whether promised opportunities will materialize. Local leaders argue that cancelling projects risks leaving towns behind in the clean energy transition, especially those that had been preparing for new investments and growth.
8. Blue States Disproportionately Affected

Reports indicate that many of the cancelled projects were located in Democratic-leaning states, including California, New York, and others across the Northeast and West Coast. These states often lead in adopting clean energy policies.
The decision has sparked accusations that politics influenced the funding cuts. Critics say targeting projects in blue states undermines national unity on climate issues, while officials insist the cancellations were based on cost-benefit evaluations. Either way, the move deepens the divide over how the U.S. should handle its energy future.
9. Climate Goals Become Harder to Reach
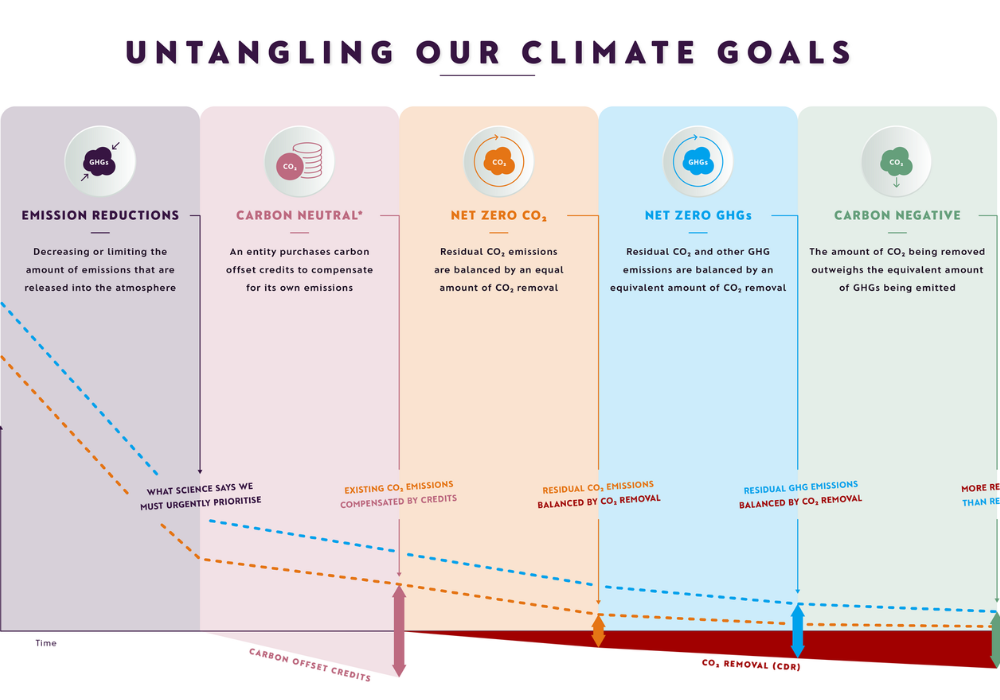
The funding cuts complicate efforts to meet both state and federal climate targets. Many of the projects were designed to help lower emissions in line with international commitments and domestic clean energy laws.
Without federal support, states may struggle to scale up renewable energy or reduce reliance on fossil fuels quickly enough. Scientists warn that delays now will make it harder to limit warming to safer levels, increasing the risks of extreme weather, rising seas, and other climate impacts.
10. Energy Costs Could Rise for Consumers

Some of the cancelled projects were designed to make energy cheaper by investing in efficiency and diversifying power sources. Losing that investment could mean higher costs for consumers in the long run.
For example, without modern grid upgrades, utilities may face more expensive repairs after weather disasters, costs that are often passed on to customers. Cancelling programs that would have boosted local clean energy production could also increase dependence on fossil fuels, which remain vulnerable to volatile global markets.
11. Debate Over National Priorities Intensifies

The cancellations have reignited debate over how much the U.S. should invest in climate solutions. Supporters of the cuts argue that funding must be carefully scrutinized and that taxpayer money should not be wasted on projects with uncertain outcomes.
Opponents counter that cutting billions now will cost much more later, as climate-driven disasters grow more expensive and communities miss out on jobs and innovation. The debate underscores a broader question: whether the U.S. will lead or lag in the global race toward clean energy.
