New research suggests the universe may one day collapse in a dramatic cosmic reversal.

Scientists studying the fate of the cosmos have proposed a surprising possibility: the universe may not expand forever after all. New calculations suggest dark energy—the mysterious force pushing galaxies apart—could one day weaken, eventually reversing its effect. If that happens, expansion would slow, stop, and then run backward, leading to a catastrophic collapse billions of years in the future. Though the idea remains theoretical, it challenges long-held assumptions about the universe’s distant timeline and raises major questions about how everything we know might ultimately end.
1. Dark Energy Controls the Universe’s Expansion

Researchers emphasize that dark energy is the key force shaping the destiny of the cosmos. It currently accelerates the expansion of space, pushing galaxies farther apart at increasing speed. While dark energy makes up most of the universe, scientists still don’t fully understand how it works or why it behaves the way it does.
The new study explores what could happen if dark energy begins to weaken over time. Even a small shift in its strength could dramatically alter the long-term trajectory of the universe.
2. The Universe Could Stop Expanding Billions of Years from Now

According to the model explored by researchers, dark energy may not stay constant forever. If it loses power, the universe’s expansion would gradually slow down. Eventually, the outward push from dark energy could fall to zero, marking a turning point for the entire cosmos.
This slowing could take billions of years, but the change would signal the end of the expansion era. Scientists say this scenario remains hypothetical but possible within current physics.
3. A Reverse Expansion May Lead to a Cosmic Collapse

If dark energy weakens enough, the universe’s expansion could reverse entirely. Instead of galaxies racing apart, gravity would slowly pull everything back together. This reversal would unfold over extremely long timescales, beginning with a gradual shift in cosmic motion.
Researchers call this scenario a “big crunch,” where the universe ultimately collapses inward. Such an event would represent the opposite of the Big Bang that started everything.
4. A Collapse Could Occur in About 33 Billion Years

Based on the study’s mathematical models, a reversal of expansion could begin as early as 65 million years from now, which is extremely soon on cosmic timescales. If the process starts, the full collapse could occur around 33 billion years in the future.
These numbers are highly theoretical and depend on assumptions about dark energy. Still, they offer a framework for understanding how the universe might evolve.
5. Scientists Stress That the Theory Is Not a Prediction

Researchers caution that their model is not a certainty. Dark energy is still poorly understood, and alternative theories suggest the universe could expand forever or tear itself apart. The current study simply shows that a collapse is mathematically possible if certain conditions occur.
Scientists expect that future observations will help refine these models. For now, the universe’s fate remains an open question.
6. The Big Crunch Is One of Several Possible Endings

The collapse scenario is just one potential outcome among many proposed by physicists. Other possibilities include the “heat death,” where the universe cools and expands forever, or the “big rip,” where dark energy grows so strong that it tears galaxies apart.
Each outcome depends on how dark energy behaves over time. The new research adds another scenario to the list, broadening the discussion about the cosmos.
7. New Data Could Change Our Understanding of Dark Energy
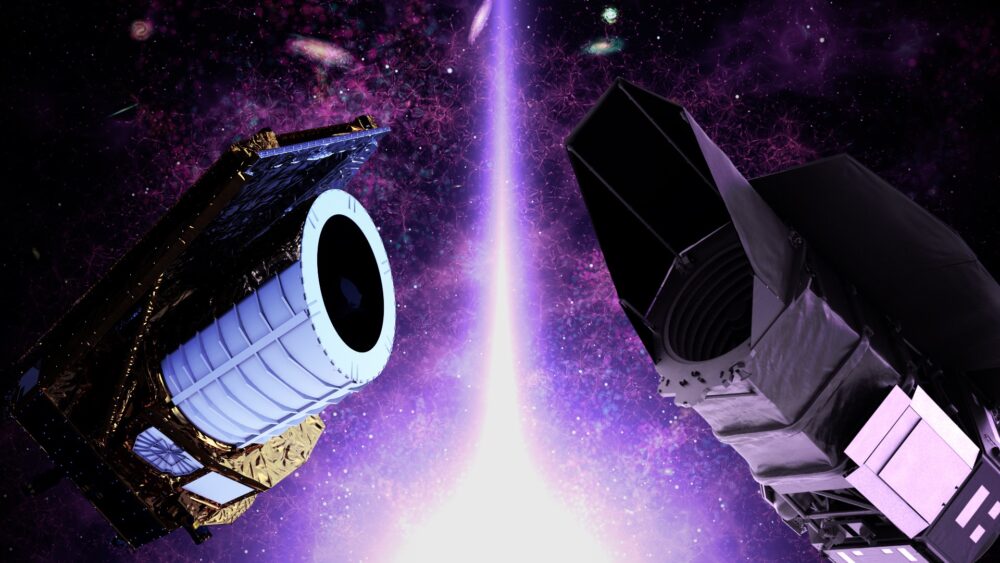

Scientists hope future telescopes and cosmic surveys will reveal whether dark energy is constant or evolving. Projects like NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope and the European Space Agency’s Euclid mission are designed to study the universe’s expansion in detail.
These observations will help determine whether dark energy may weaken in the future. The answers could reshape long-term theories about the fate of the cosmos.
8. Cosmic Collapse Would Reverse Billions of Years of Expansion

If a collapse begins, galaxies that spent billions of years drifting apart would start moving closer again. Over vast timescales, this reversal would affect the structure of the entire universe. Stars, planets, and black holes would be drawn toward a central point.
This process would dramatically change the cosmic environment. Eventually, temperatures would rise as matter compresses, setting the stage for a final, catastrophic end.
9. The End Stages Could Mirror the Conditions of the Big Bang

As the universe collapses, temperatures and densities could climb to extreme levels. Some physicists suggest the final moments of a big crunch might resemble the conditions present before the Big Bang, when all matter was concentrated in a tiny, hot point.
This concept raises questions about whether the universe could restart in a new cycle. Researchers continue to debate whether such a “bounce” is possible.
10. The Theory Encourages New Ways of Thinking About the Cosmos
Regardless of whether a collapse ultimately occurs, the study challenges scientists to rethink assumptions about dark energy and the universe’s future. It underscores how little is known about the forces shaping cosmic evolution.
This research also highlights the importance of continuing to study distant galaxies and the expansion of space. Each discovery adds another piece to the puzzle of how the universe began—and how it might one day end.
