Robots are crossing the line between machine and human—and it’s eerie.

Robots are evolving beyond mechanical functions to exhibit more human-like behaviors and designs. Through breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensory technology, machines now communicate fluidly, recognize emotions, and adapt to complex environments. While their appearance can be humanoid, these advancements focus on genuine interaction improvements rather than mere imitation. Understanding these developments clarifies the profound ways robots are becoming companions, assistants, and collaborators in daily life.
1. Robots are improving their natural language skills to hold conversations smoothly.

Natural language processing technologies enable robots to engage in conversations that feel fluid. By analyzing syntax and semantics, these systems allow machines to navigate dialogue with a grace once thought impossible. Short questions can be handled smoothly, enhancing human-robot rapport.
This conversational fluidity leads to robots successfully operating in customer service and support roles. A busy cafe, where a robot barista takes orders, exemplifies the integration of machine language skills into real-life scenarios. Such interactions demonstrate expansive progress in human-robot communication.
2. Machines are learning to recognize and respond to human emotions accurately.
Machines enhance their emotional comprehension through algorithms that assess facial expressions and vocal cues. Emotional recognition systems decipher subtle hints of happiness or frustration. The ability to detect these nuances allows robots to adjust their responses accordingly, mirroring human conversational adaptability.
In healthcare settings, these technologies enable robots to support patient wellbeing by offering comfort through tailored interactions. By reading a patient’s concerned expression, a robot might deploy soothing words or actions. The intended effect is a more empathetic robotic presence.
3. Robots are developing more fluid and natural body movements for interaction.

Engineers are refining the design of robotic joints to mimic human-like fluidity. Utilizing advanced servomotors, robots achieve more seamless motion, shedding the once herky-jerky, mechanical demeanor. The balance between form and function becomes tangible in graceful gestures that invite engagement.
These advancements find particular success in assistive technologies, where smooth movement helps bridge the gap between machine and human. In rehabilitation, a robot’s ability to mimic human motions can support patients’ physical therapy, making the technology a valued ally.
4. Artificial intelligence helps robots better understand and predict human behavior.
Artificial intelligence empowers robots to grasp the intricacies of human behavior, analyzing patterns to anticipate needs. Algorithms unlock predictive capabilities, allowing for better alignment with a person’s actions or habits. This fosters a richer interaction experience between humans and robots.
In homes, smart devices harness these abilities to predict when homeowners return, adjusting lighting or climate in anticipation. Such intuitive understanding transforms the once passive machine into an active participant, bridging the experiential divide.
5. Robots are gaining enhanced visual perception for interpreting complex environments.
Enhanced visual perception is enabling robots to decode complex environments effectively. By incorporating cameras and sensors, robots interpret a cluttered kitchen or a busy street, navigating with finesse rather than fumbling. This visual acuity promotes seamless interactions in dynamic settings.
Such advancements empower service robots in hospitality to weave through bustling venues without collisions. Understanding space and movement allows robots to operate independently, enhancing functionality beyond simple tasks to more sophisticated forms of engagement.
6. Advances in touch sensors allow robots to respond to physical contact gently.

Precision touch sensors afford robots a delicate grasp on physical interaction. Mimicking human touch, these sensors help machines adjust their force aptly when handling objects or humans. This tactile refinement grants robots the tact needed for delicate operations without discomfort.
In eldercare, these sensors enable robots to assist seniors safely with dressing, demonstrating a compassionate utility. The tactile language of touch speaks volumes in caregiving, laying a foundation for responsible robotic help that respects human fragility.
7. Robots are being programmed to exhibit empathy during social interactions.

Empathy-directed programming equips robots with cues for social awareness during interactions. By scripting responses such as smiling or nodding, robots cultivate a semblance of emotional depth. These programmed behaviors create a more relatable and accessible presence during human interactions.
Such empathy plays a vital role in therapeutic settings, where robots participate in workshops to enhance social skills for children. Here, robots provide non-judgmental companionship while reinforcing positive behaviors and fostering learning through interaction.
8. Machine learning enables robots to adapt their responses over time.
Machine learning algorithms continuously refine a robot’s decision-making processes. Feedback loops train robots, enabling them to adapt responses based on prior experiences. This ongoing learning empowers robots to offer more personalized interactions over time, surpassing static programmed behaviors.
From adaptive customer service robots in retail to tutors offering individualized learning paths, this adaptability illustrates a significant leap in robotic usability. Each interaction enriches the robot’s repository of experiential learning, tailoring future engagements considerately.
9. Robots are becoming better at recognizing individual human faces reliably.
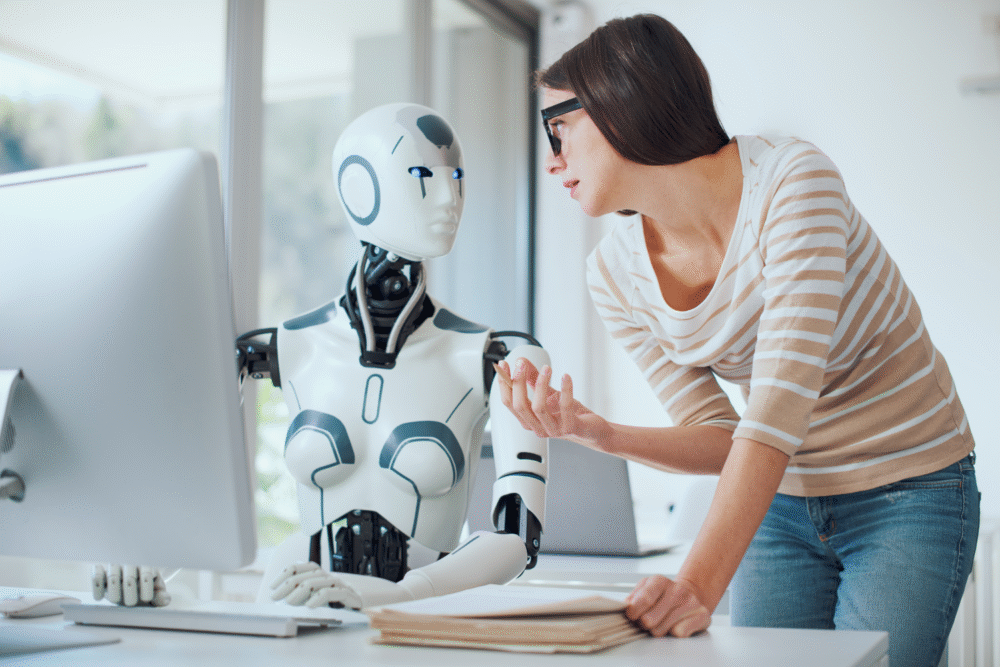
Facial recognition tech allows robots to identify individuals reliably, using unique facial features. This consistency in recognition supports security and personalized interactions in both public and private domains. Recognition fidelity hinges on advancements in machine vision technologies.
In personalized services, robots use facial recognition to remember customers’ preferences, creating a bespoke experience in hospitality or retail. Robotics’ ability to distinguish faces accurately strengthens trust in practical applications, enhancing security while preserving personalization.
10. Robots can now interpret tone and context to improve communication.

Robots interpret tone and context with rising sophistication, utilizing spectral analysis to decipher subtext in communication. This nuanced comprehension transforms interactions, beyond content words alone. Tone recognition aligns with contextual cues, favoring more nuanced, relevant exchanges.
Error correction in real-time enables smarter responses. In legal mediation, a robot detecting rising tension it might employ calibrated language to maintain neutrality while soothing tempers, showcasing its communicative adeptness and its role in delicate negotiations.
11. Emotional intelligence is being integrated into robots for more natural engagement.
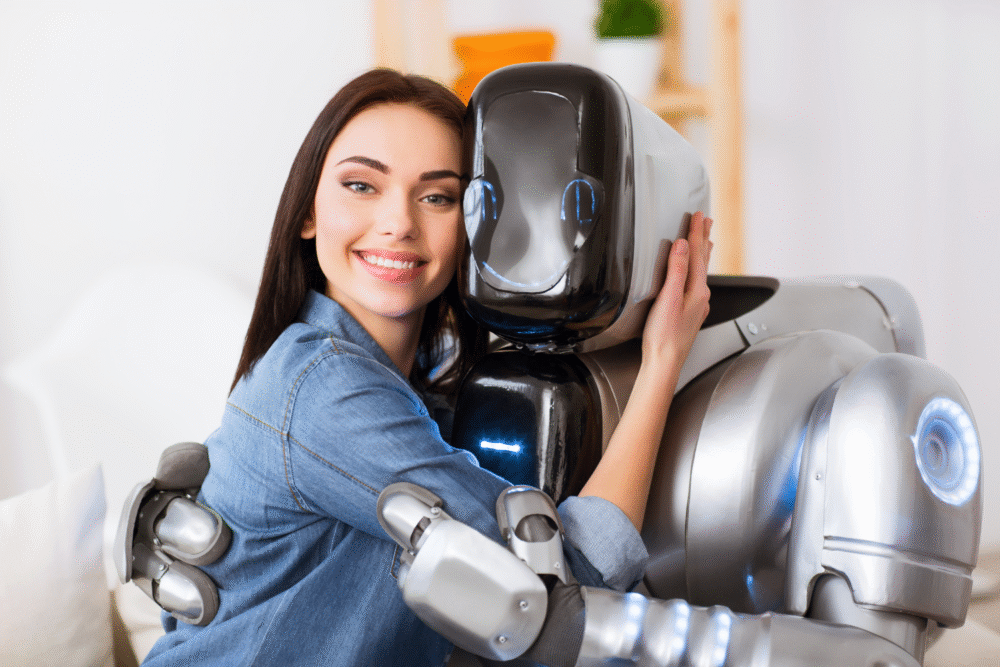
Integrating emotional intelligence into robots helps craft more engaging interactions. By mirroring human emotional responses, robots gain an edge in their engagement capability. Systems detecting mood nuances provide machinery an emotional compass, guiding conversation placidly during interactions.
For educational purposes, robots with emotional awareness assist reluctant learners. By providing feedback tuned to a student’s potential frustration or enthusiasm, robots maintain a conducive learning atmosphere, thus enriching educational experiences across age groups.
