Analysts say some U.S. cities could face rapid collapse if widespread unrest overwhelms vital systems.

A new analysis of urban infrastructure, population density, and social vulnerability suggests that some American cities could change dramatically within hours if widespread civil unrest were to erupt. Experts point to factors like aging power grids, limited evacuation routes, and deep political divisions that could turn demonstrations into cascading crises. While researchers stress that such scenarios are unlikely, they warn that recent years have revealed just how fragile modern cities can become under extreme social pressure.
1. Researchers Are Studying How Quickly Cities Could Break Down

Urban planners and sociologists have modeled how major U.S. cities might respond to sudden, large-scale unrest. Their findings show that densely populated areas with strained infrastructure could see services like transportation, communication, and policing falter within hours.
The models are based on real-world events—from natural disasters to major protests—that disrupted essential systems. While the scenarios are theoretical, experts say they highlight how even the most modern cities depend on fragile, interconnected networks that can quickly unravel under stress.
2. Large Metro Areas Are the Most Vulnerable

Cities such as Los Angeles, New York, Chicago, and Houston face higher risks of rapid disruption because of their population density and reliance on complex infrastructure. In these cities, a breakdown in one area—like power or transit—can trigger cascading effects throughout the region.
Emergency planners note that these metros have strong response teams but also greater challenges in maintaining order across sprawling neighborhoods. Once public transport halts or communication networks go down, mobility and coordination become nearly impossible.
3. Aging Power Grids Could Exacerbate a Crisis

Many U.S. cities rely on power systems that are decades old and already under heavy strain from extreme weather, cyber threats, and high demand. If unrest or sabotage targeted substations or transmission lines, outages could spread far beyond the immediate area.
Without power, traffic lights fail, ATMs stop working, and communication networks collapse. Experts say even brief blackouts can worsen unrest by limiting information, disrupting emergency response, and creating widespread confusion among residents.
4. Transportation Systems Are a Critical Weak Point

Urban mobility depends on subways, buses, and highways—all of which can be disrupted by demonstrations, accidents, or blockades. A few key choke points can paralyze entire cities if bridges, tunnels, or major intersections become inaccessible.
Studies show that cities like Washington, D.C., and San Francisco could gridlock within hours if mass gatherings or power failures shut down transit routes. Once roads clog and public transport halts, emergency services struggle to move, further amplifying chaos.
5. Economic Centers Could Face the Fastest Disruption
Cities with concentrated financial districts—such as New York, Dallas, and Atlanta—are particularly exposed to cascading economic impacts. A brief shutdown of trading hubs, data centers, or logistics networks could freeze commerce almost instantly.
Researchers warn that even short-term paralysis in these sectors could trigger national ripple effects, disrupting supply chains and digital infrastructure that support millions of Americans. Financial markets and online payment systems remain highly centralized, making them vulnerable to localized unrest.
6. Social Division Adds to the Risk

Experts emphasize that social cohesion—trust between communities and institutions—is a city’s most powerful stabilizer. In areas where inequality, political polarization, or racial tension runs deep, small incidents can ignite widespread unrest.
Cities that already experience high levels of protest activity or distrust in government may find it harder to maintain calm. Analysts note that strong community leadership and transparent communication are key to preventing demonstrations from turning into full-scale crises.
7. Law Enforcement Capacity Would Quickly Be Tested

Even large police departments can become overwhelmed when unrest spans multiple districts. In 2020, major U.S. cities reported that dispatch response times doubled or tripled during periods of mass protest.
If unrest intensified citywide, local agencies would depend on state and federal support—but mobilizing that help takes time. Experts recommend pre-established coordination plans and mutual-aid agreements to avoid delays that allow violence or looting to spread unchecked.
8. Information Overload Could Amplify Chaos
During any major crisis, social media plays a double-edged role: it can both inform and inflame. Misinformation spreads quickly, fueling panic or false narratives that hinder authorities’ ability to respond effectively.
Researchers from MIT and Stanford found that unverified online claims during past protests increased crowd sizes and redirected movements within minutes. The speed at which digital misinformation spreads means that modern unrest could evolve faster than official communication can keep pace.
9. Food and Fuel Shortages Would Develop Within Days
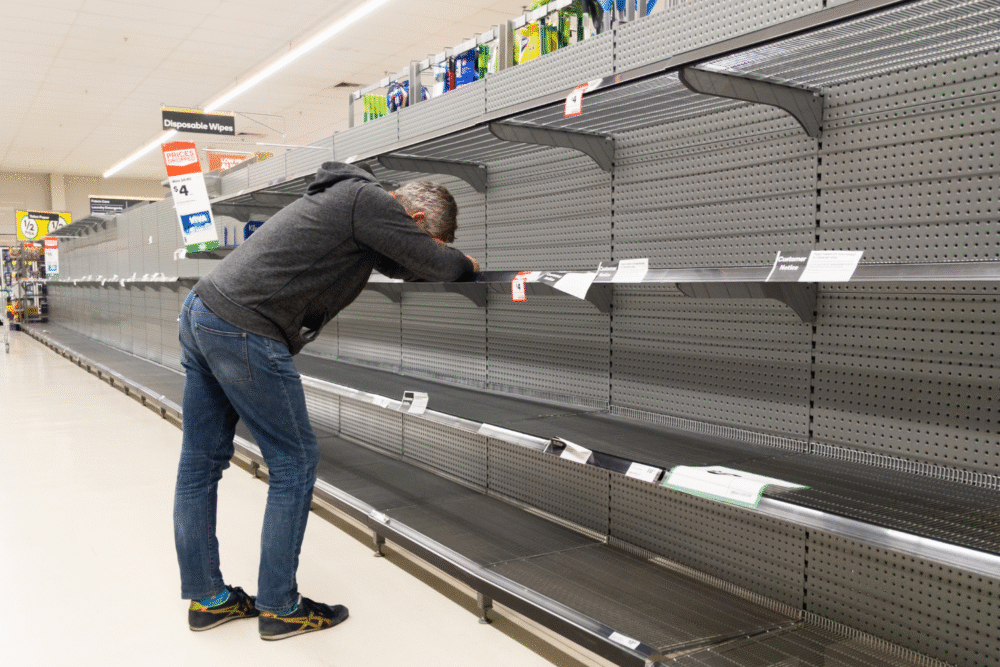

Urban supply chains operate on tight schedules, with grocery stores and gas stations typically holding only a few days’ worth of inventory. If unrest disrupts trucking routes or warehouse access, shortages could emerge within 48 to 72 hours.
Experts note that most major cities rely heavily on just-in-time delivery systems, leaving little room for error. If deliveries stop—whether from blockades, curfews, or road closures—residents could face empty shelves and rising tension in a matter of days.
10. Critical Services Would Struggle to Function

Hospitals, fire departments, and emergency shelters all depend on reliable power, transportation, and communication. If multiple systems failed simultaneously, even routine emergencies could become deadly.
Public health experts warn that a surge in injuries, combined with limited mobility, could overwhelm hospitals within hours. Maintaining access to clean water, medication, and emergency care would become a top priority, especially in older cities where facilities are already at capacity.
11. Smaller Cities Could Be More Resilient

Interestingly, analysts say some smaller or mid-sized cities may be better equipped to maintain order. Their lower population density, tighter community networks, and shorter supply chains make coordination easier during emergencies.
Towns with strong local leadership and civic engagement tend to recover faster from crises. Experts highlight examples like Minneapolis and Portland, where rapid local cooperation helped restore essential services after periods of unrest. Adaptability and communication are key survival factors.
12. Preparedness, Not Panic, Is the Goal

Despite alarming models, experts stress that these scenarios are designed to inform resilience planning—not predict imminent chaos. They serve as a warning about how fragile urban systems can be and how quickly interdependence can turn strength into vulnerability.
Researchers urge city leaders to invest in disaster-response infrastructure, emergency communication systems, and community trust. The takeaway, they say, isn’t fear—it’s readiness. Understanding these risks today could prevent a true breakdown tomorrow.
