Something unusual is happening beneath China’s vast fields of solar panels.
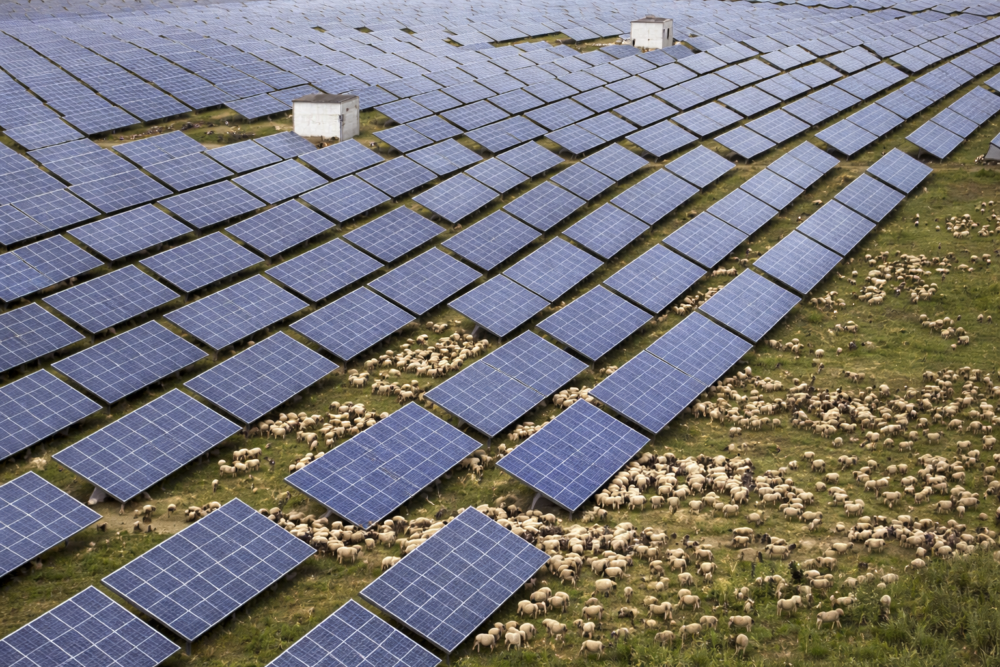

China’s largest solar farm stretches across the arid highlands of Qinghai Province, on the northeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Built on land long considered too harsh for large-scale development, the vast installation was designed to generate clean electricity at an unprecedented scale and reduce reliance on coal.
But scientists studying the site have noticed something unexpected happening beneath the panels. The desert landscape below is changing, with subtle shifts in soil moisture, temperature, and plant growth that differ from nearby untreated areas.
What began as a massive energy project in one of China’s driest regions is now offering new insight into how renewable infrastructure can quietly reshape the environments where it is built.