Genetic breakthroughs are pushing human potential to the next level.

Genetic engineering is no longer the stuff of science fiction. It’s already transforming the way we treat disease, fight aging, and even enhance our bodies beyond what nature intended. Scientists are making DNA tweaks that could eliminate genetic disorders, supercharge immune systems, and even slow down aging. Some of these breakthroughs are already saving lives, while others remain highly controversial.
The potential for genetic engineering is staggering. New treatments are emerging faster than regulators can keep up, promising to reshape medicine forever. While some worry about the ethical implications, others see an opportunity to eliminate suffering and extend human potential. This technology isn’t waiting for approval, and those willing to embrace it could be the first to experience its life-changing potential. These 11 innovations aren’t just ideas—they’re redefining health, medicine, and what it means to be human.
1. Scientists are scrubbing diseases from DNA like typos in a text.
Some genetic conditions have haunted families for generations. CRISPR is changing that. This gene-editing tool is already being used to remove inherited diseases like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and even certain cancers before a child is even born.
By cutting out faulty genetic sequences and swapping them for healthy ones, scientists are essentially proofreading human DNA. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reports that CRISPR-based gene therapies have already been approved to treat sickle cell disease, marking a major step in the fight against inherited conditions. The possibilities are staggering—future generations could be free from conditions that were once considered inescapable. But editing embryos raises significant ethical questions.
If we can eliminate disease, where do we draw the line? While researchers are moving cautiously, one thing is clear: preventing genetic diseases before birth isn’t science fiction anymore—it’s happening.
2. Your DNA might soon get a software update to fix genetic glitches.

Living with a genetic disorder has always meant working around it, but gene therapy is rewriting that reality. Instead of just managing symptoms, scientists are now fixing faulty DNA inside living cells, offering potential cures for conditions like muscular dystrophy, hemophilia, and inherited blindness. Think of it as debugging your biological code.
Some treatments replace broken genes, while others switch off harmful mutations or introduce new instructions that help the body heal itself. According to Harvard Medical School, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a CRISPR-based gene therapy developed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics, which has shown significant success in treating sickle cell disease. The biggest challenge? Cost. But as the technology advances, permanent cures for genetic conditions could become just another routine doctor’s visit.
3. Vaccines are no longer just training your immune system—they’re rewriting it.

Traditional vaccines teach your immune system how to fight infections. The next generation is taking it further, using genetic technology to reprogram your body’s defenses from the inside out. Instead of injecting weakened viruses like conventional vaccines, genetic vaccines instruct your cells to make specific proteins that trigger immunity. This approach could create stronger, longer-lasting protection with just one shot.
Scientists are now testing DNA-based vaccines for conditions like multiple sclerosis and even Alzheimer’s. Research from UT Southwestern Medical Center found that a DNA vaccine reduced toxic protein buildup linked to Alzheimer’s in mice, avoiding the severe brain swelling seen in past treatments. While the idea of tweaking DNA makes some people uneasy, early results suggest these vaccines could eliminate some of the world’s deadliest diseases within a generation.
4. The spare parts industry is moving into human organs.
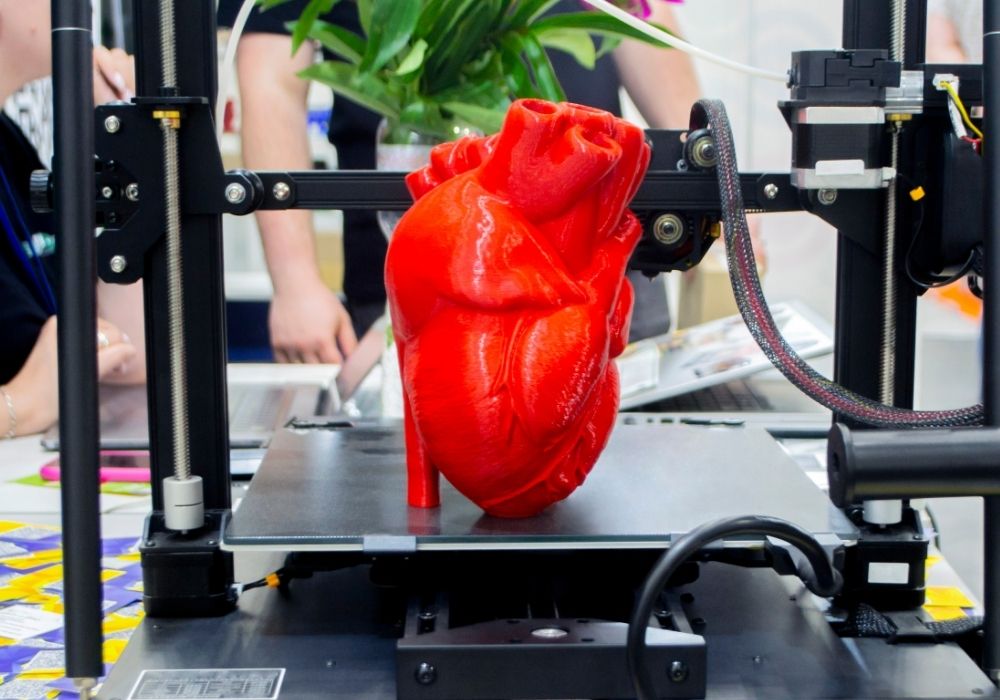
Transplant lists might soon be a thing of the past. Scientists are already growing human tissues in labs, and entire organs may not be far behind. Thanks to bioprinting and stem cell breakthroughs, hospitals could one day be printing hearts, kidneys, and livers on demand.
Using living cells as ink, researchers are layering them onto 3D scaffolds to build complex tissues. Some lab-grown body parts—like corneas and blood vessels—are already being tested in patients.
The biggest challenge is making fully functional, transplantable organs. But if science pulls it off, waiting for a donor match could become a thing of the past, and rejection risks could be significantly reduced. The future of organ transplants might not involve another human—it might involve a printer.
5. Scientists are finding ways to press “pause” on aging.

What if getting older was optional? Genetic researchers are now targeting the aging process at its deepest level—your DNA. By tweaking genes linked to longevity, they’ve already extended the lifespans of mice by 30%, and human trials are on the horizon. Some gene therapies are focused on repairing damaged DNA, while others stimulate cell regeneration or slow down the biological clock that leads to aging.
Early studies have shown promising results, with some treatments reversing signs of aging at the cellular level. While billionaires race to fund longevity startups, scientists are working on making these treatments accessible to more than just the ultra-rich. If they succeed, we may have to start redefining what it means to grow old.
6. Food allergies could soon be as outdated as dial-up internet.
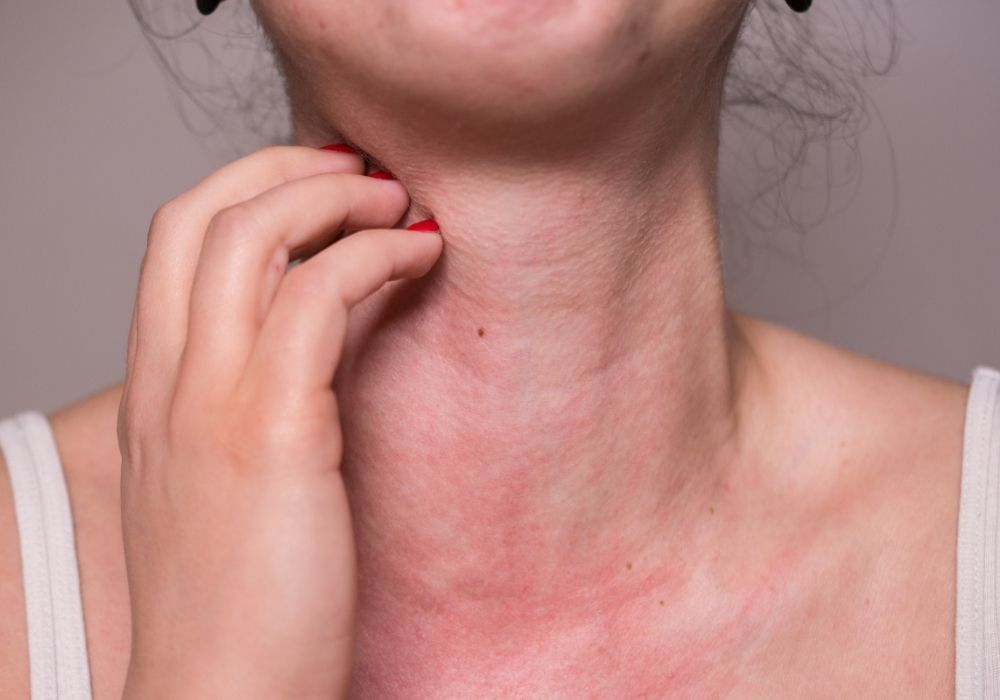
For millions of people, something as simple as eating a peanut could be life-threatening. But thanks to gene editing, allergies might soon be erased at their root cause.
Scientists are working on CRISPR-based therapies that target the genes responsible for immune system overreactions, essentially switching off dangerous allergies. Unlike allergy shots, which require lifelong maintenance, this treatment could permanently reprogram the body’s response to allergens.
Early trials have already reversed severe peanut allergies in mice, and human testing isn’t far behind. If successful, future generations might grow up never knowing what it’s like to scan ingredient lists or carry an EpiPen everywhere they go.
7. The next superheroes might be engineered, not born.

Certain people bounce back from illness at an unbelievable speed, rarely getting sick while others struggle with constant infections. Scientists are working on ways to make that kind of immunity universal.
By modifying immune cells at the genetic level, researchers are designing stronger defenses against infections, autoimmune diseases, and even cancer. The military and biotech industries see enormous potential in this research, not just for public health but also for performance enhancement. Instead of relying on vaccines or medications, the body itself could be upgraded to fight off threats before they ever take hold.
8. Cancer treatments are getting personal—because they’re built from your DNA.
A new era of cancer treatment is unfolding, shifting away from one-size-fits-all approaches toward therapies designed specifically for each patient. Genetic engineering is leading the way, creating treatments that pinpoint and attack cancer at its root.
These advancements rely on sequencing a patient’s DNA to identify the exact mutations driving tumor growth. With this information, doctors can develop targeted therapies that train the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Treatments like CAR-T therapy, which reprograms immune cells, are already changing outcomes for patients who had no other options. As these innovations become more accessible, cancer treatment is moving toward a future where the body’s own genetic code holds the key to survival.
9. Scientists are hacking muscle growth, no gym required.

Massive gains in muscle strength don’t always come from intense training. Some rare genetic mutations give people naturally enhanced muscle mass, and researchers are now figuring out how to harness that advantage for everyone.
Gene therapy trials originally developed to treat muscular dystrophy are showing promising results for increasing muscle growth and endurance. In early experiments, animals with edited genes displayed significantly stronger, more resilient muscles. While medical applications are the primary focus, the fitness world is already paying close attention. If this research continues advancing, muscle-building could shift from lifting weights to flipping genetic switches.
10. Genetics are being rewritten, and dieting may never be the same.

Losing weight has always been a battle of willpower, but genetics play a bigger role than most realize. Researchers are now targeting the DNA responsible for metabolism, hunger, and fat storage to make maintaining a healthy weight easier.
Scientists have discovered genetic pathways that influence how efficiently the body burns calories. By tweaking these pathways, gene-based treatments could prevent excessive fat accumulation and naturally regulate appetite.
This research is advancing quickly, raising possibilities that could render fad diets and weight-loss gimmicks obsolete. Instead of endless calorie counting, people may soon have access to therapies that allow their genetics to work in their favor.
11. Human potential is getting an upgrade, and the future might look unrecognizable.

Genetic engineering is no longer just about curing disease—it’s laying the foundation for enhancing the human brain. Researchers are uncovering ways to boost cognitive function, improve memory, and accelerate learning through targeted DNA modifications. Specific gene expressions have been linked to intelligence, focus, and mental agility, and biotech startups are already developing therapies aimed at fine-tuning these traits.
Originally designed to treat neurological disorders, these advancements are now being explored for their potential to expand human capability beyond medical needs. As scientists push forward, the definition of natural talent is evolving, setting the stage for a future where cognitive enhancement is as routine as laser eye surgery.
