Scientists identify ten potential disasters with far-reaching global consequences and impacts.

Scientists from leading agencies like NASA, USGS, and the IPCC warn of catastrophic disasters that could profoundly impact life on Earth. These events range from natural phenomena such as supervolcanic eruptions and megathrust earthquakes to human-influenced risks like cyberattacks and nuclear conflict. Understanding these hazards helps communities prepare, mitigate risks, and develop emergency responses rooted in scientific research and global cooperation.
1. Massive asteroid impact threatening widespread devastation on Earth.

A massive asteroid impact could unleash widespread devastation, characterized by its forceful explosion and dust clouds. While millions of years ago such impacts reshaped Earth’s ecology, today’s concern lies in their potential to obliterate entire regions and disrupt global systems.
In the realm of celestial events, the prospect of an asteroid collision underscores humanity’s vulnerability. Though the odds appear slim, preparation and monitoring are crucial as scientists develop strategies to detect and potentially intercept hazardous asteroids, mitigating their catastrophic potential.
2. Supervolcanic eruption causing global climate disruption and air pollution.

Supervolcanoes, hidden under thick crusts, have the power to eject vast quantities of ash and gas into the atmosphere. Such eruptions can dim sunlight globally, leading to climate disruptions and significant agricultural collapse. Ash-laden skies become a stark symbol of nature’s force.
The long-term consequences of a supervolcanic eruption are serious: crop failures and temperature drops could persist for years. Understanding these eruptions aids in assessing their impact on human civilization, encouraging international cooperation and ongoing volcanic monitoring.
3. Global pandemic spread by a highly contagious and lethal virus.

A global pandemic involving a highly contagious and deadly virus could strain healthcare systems and disrupt daily life. As seen with past outbreaks, rapid human and economic mobilization defines science and community response to limit spread and impact.
History provides glimpses of society’s striking ability to innovate and adapt in the face of pandemics. Concerted global efforts strengthen detection and containment strategies, highlighting the necessity for vigilant public health infrastructures capable of responding to unprecedented viral threats.
4. Large-scale nuclear conflict leading to catastrophic environmental consequences.
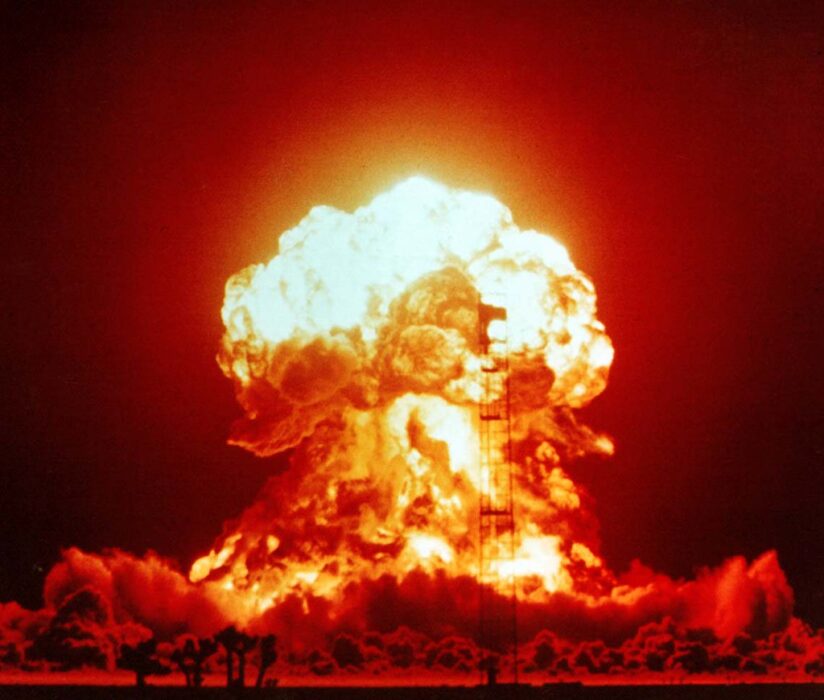

A large-scale nuclear conflict poses unimaginable environmental and human risks, with explosions releasing devastating radiation and heat. The resulting fires and fallout complicate ecosystems for decades, potentially inducing nuclear winter scenarios that dampen sunlight and disrupt global weather patterns.
Comprehending nuclear conflict’s dire consequences emphasizes the importance of diplomacy to prevent escalation. Specialists advocate for arms control and disarmament as protective measures against environmental catastrophes that respect no borders or diplomatic boundaries.
5. Extreme solar storm disrupting power grids and communication systems.
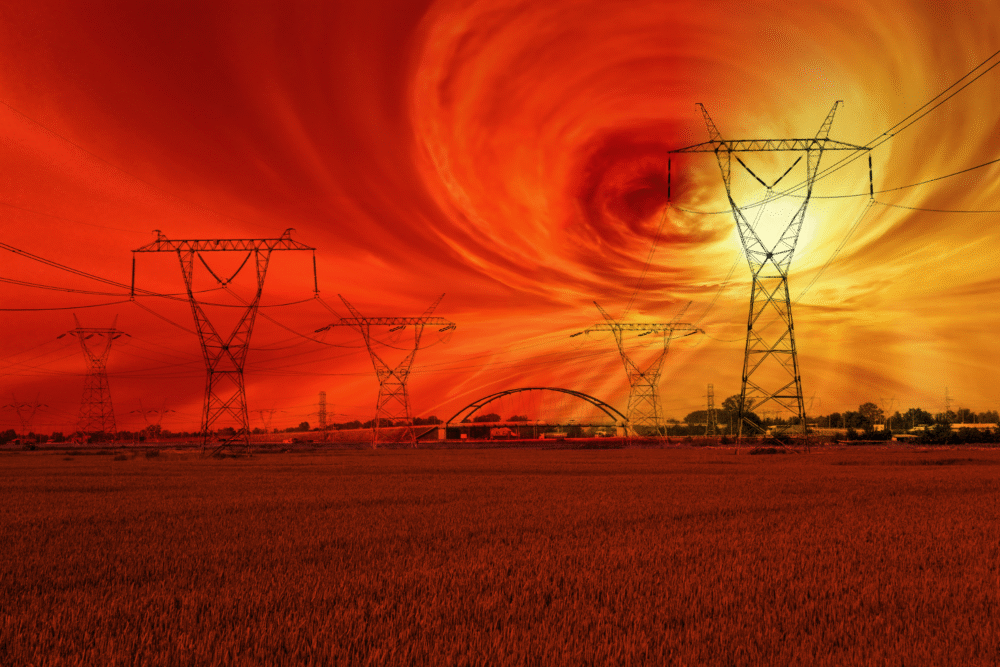

Extreme solar storms release powerful electromagnetic pulses capable of disabling power and communication networks. Already, past minor solar events have caused brief blackouts, providing a glimpse into potential extended outages that might paralyze modern conveniences.
When charged particles bombard Earth’s magnetic field, they can induce currents in infrastructure, frying circuits and transformers. Preparedness includes identifying vulnerabilities to bolster system resilience, ensuring that societies can withstand and recover from these celestial disturbances.
6. Rapid and severe climate change triggering food and water shortages.
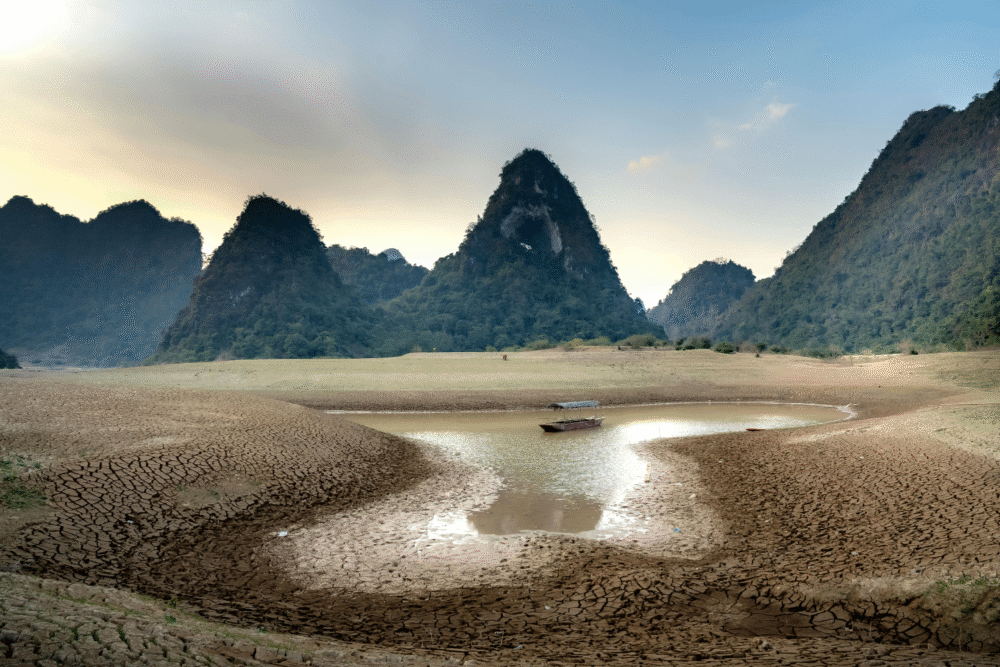

Rapid and severe climate change introduces conditions that may trigger food and water shortages worldwide. Rising temperatures and erratic weather patterns result in crop failures, water scarcity, and increased competition for dwindling resources in vulnerable regions.
The knock-on effects extend through ecosystems, influencing biodiversity and threatening community stability. Understanding climate-related impacts calls for sustainable resource management, crucial for maintaining food supply chains and ensuring access to clean water under challenging environmental shifts.
7. Megathrust earthquake striking densely populated coastal regions unexpectedly.
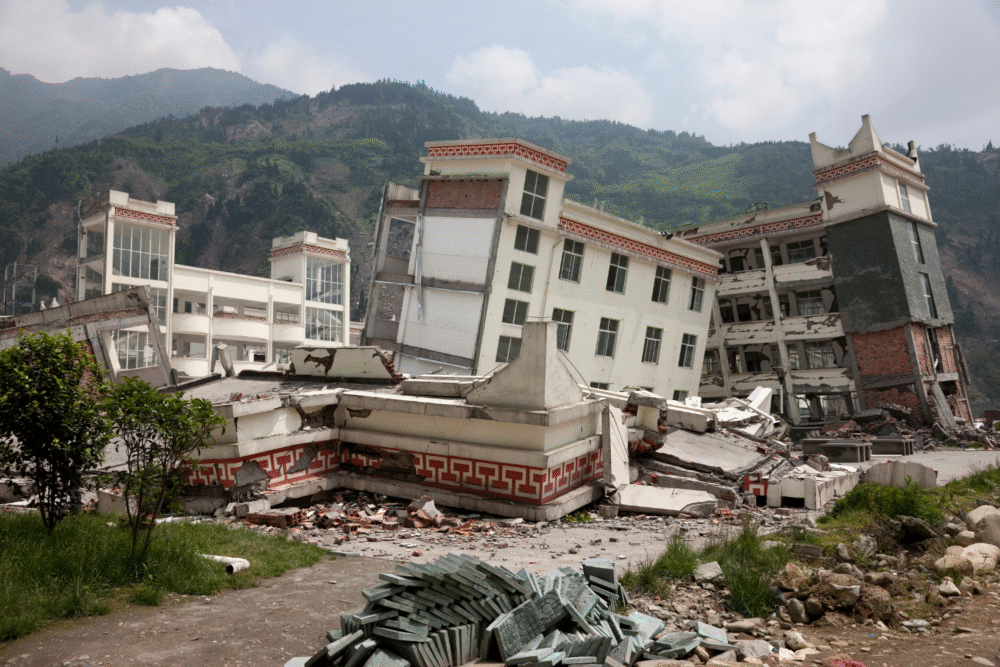

Megathrust earthquakes potent enough to shake coastlines unleash tsunamis and cause structural devastation. These massive shifts along tectonic plates can strike with little warning, as evidenced by historical earthquakes that reshaped landscapes and displaced populations.
Urban areas near fault lines face heightened risk, requiring comprehensive planning and construction codes sensitive to seismic activity. Studies of tectonic stress expand our grasp of these geophysical forces, informing strategies to minimize damage and enhance readiness.
8. Widespread failure of critical infrastructure due to cyberattacks.

The widespread failure of critical infrastructure from coordinated cyberattacks threatens basic societal functions. In our digitally connected world, disruptions to power, financial systems, and communication could rapidly escalate into societal crises, affecting day-to-day operations.
As dependency on digital assets grows, cybersecurity gains prominence. Advances in malicious software necessitate continuous deployment of rigorous security protocols, minimizing the potential fallout from cyber-induced infrastructure failures and safeguarding essential services.
9. Sudden collapse of major ice sheets causing dangerous sea level rise.
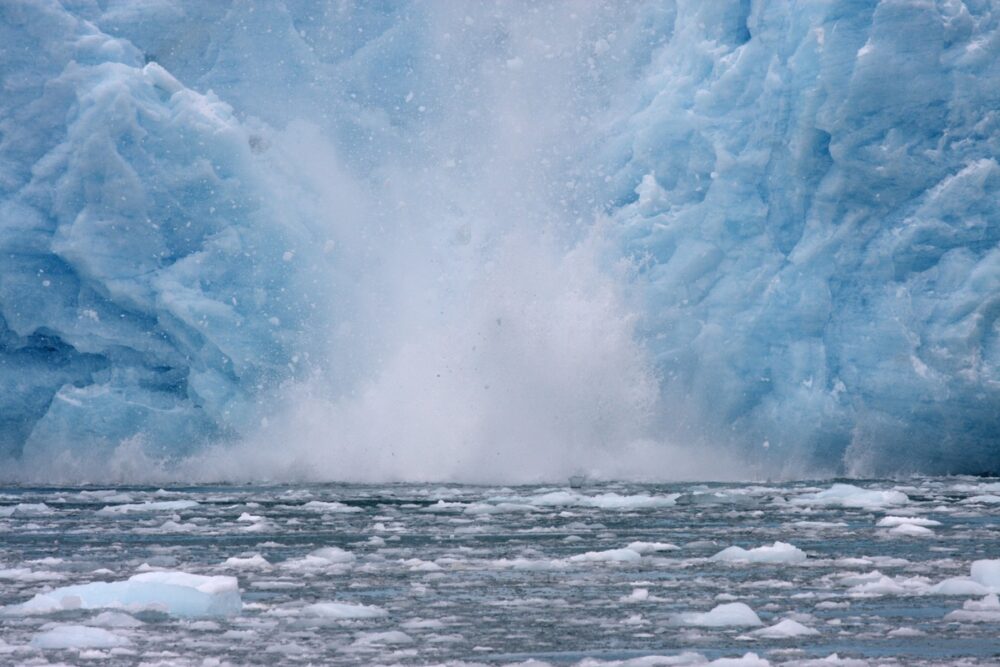

Sudden ice sheet collapse contributes to rising sea levels, posing risks to coastal communities through flooding and erosion. Ice dynamics at the poles shift ocean circulation patterns and weather systems, carrying implications for habitats across the globe.
The delicate ice balance integrates climate and environmental science. As melting accelerates, researchers prioritize predictive modeling and mitigation efforts to safeguard land and help vulnerable populations adapt to evolving coastal and climatic conditions.
10. Unexpected magnetic pole reversal affecting technology and navigation worldwide.
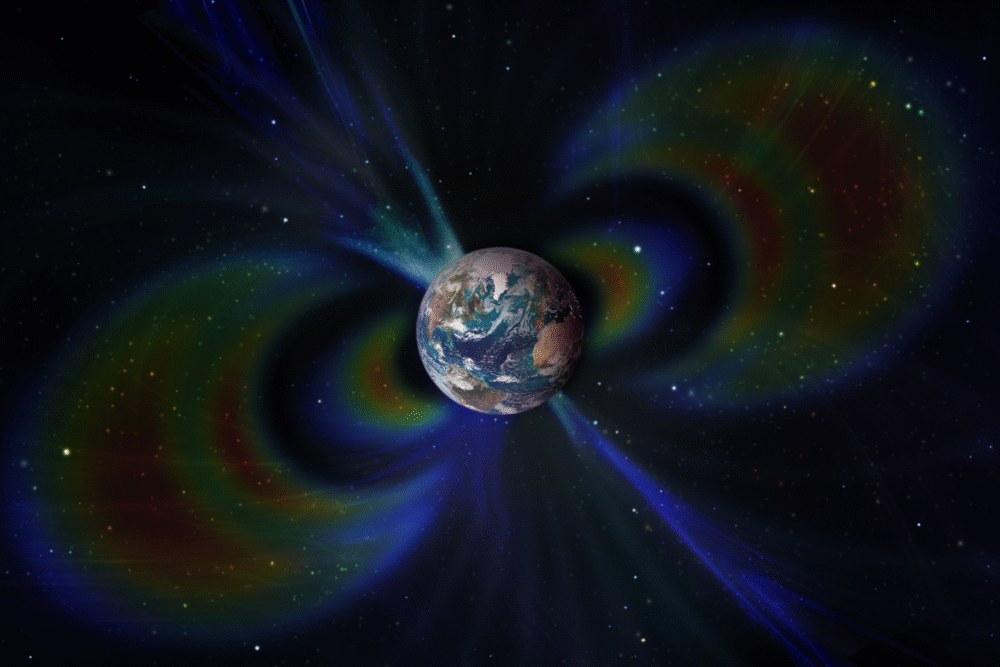
Magnetic pole reversal, though geological, could alter technological operations, challenging navigation and communication systems worldwide. The shifting of magnetic fields influences compasses, GPS, and even animal migration, demanding recalibration of devices reliant on geomagnetic coordinates.
Science unravels these enigmatic shifts through paleomagnetism, enhancing our understanding of historical reversals’ durations and effects. The adaptation of technologies to handle such changes reinforces resilience against this slow, enigmatic process affecting the worldwide technological tapestry.
