Breakthroughs in synthetic biology spark urgent debate over safety and control.

Synthetic biology is one of the fastest-growing fields in science, with researchers engineering new lifeforms that can produce medicines, clean up pollution, and even generate sustainable fuels. But alongside these breakthroughs, scientists are voicing concerns. Experts warn that lab-created organisms could behave in unpredictable ways, potentially spreading beyond intended environments or being misused. A recent report from the National Academies of Sciences highlighted the need for strong safeguards. While the technology holds enormous promise, researchers say global oversight is critical to ensure synthetic lifeforms don’t create unintended risks.
1. A Breakthrough Field With Big Questions
Synthetic biology is transforming science by allowing researchers to design and build new forms of life. These engineered organisms can be programmed to produce medicine, fuel, or even materials like plastics.
But with rapid innovation comes new risks. Experts warn that lab-created organisms could evolve in unexpected ways or spread outside controlled environments. This dual nature—immense promise paired with real danger—is why many scientists are calling for strict oversight before synthetic biology advances too far.
2. How Synthetic Lifeforms Are Created

Synthetic biology combines genetic engineering with computer modeling to design new organisms from scratch. Scientists can insert, delete, or reprogram DNA to create lifeforms that perform specific tasks.
Some organisms are designed to fight disease or produce sustainable food. Others can break down pollutants in soil or water. While these possibilities are groundbreaking, experts caution that building entirely new lifeforms pushes biology into uncharted territory. That uncertainty is why researchers urge careful regulation and global monitoring.
3. The Promise of Medical Innovation

One of the most celebrated uses of synthetic biology is in healthcare. Scientists are developing engineered microbes that can deliver drugs directly inside the body or produce vaccines faster than traditional methods.
This approach could revolutionize medicine by making treatments cheaper, quicker, and more precise. However, experts stress that medical applications must be tightly controlled. Organisms designed to save lives could cause harm if they mutate or escape into natural ecosystems, creating new challenges rather than solutions.
4. Fueling the Future With Synthetic Organisms
Researchers are engineering microbes that can produce renewable fuels from feedstocks like sugar, algae, and even waste products. This breakthrough could reduce dependence on fossil fuels and cut global carbon emissions.
Energy companies and governments are watching closely as these technologies mature. Yet experts warn that large-scale deployment requires caution. Engineered organisms could interact with natural ecosystems in unpredictable ways, raising safety and environmental concerns. Synthetic biology may help fight climate change, but only if safeguards keep pace with innovation.
5. Cleaning Up Pollution With Engineered Life
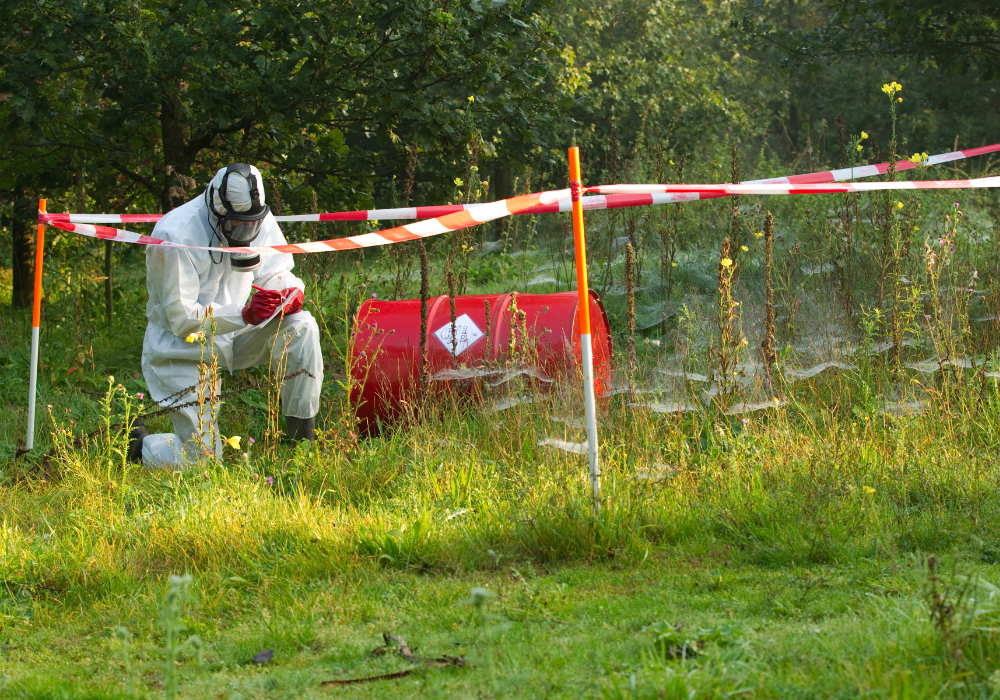

Another promising application of synthetic biology is bioremediation. Scientists are creating organisms that can break down plastics, toxic chemicals, and oil spills faster than natural processes allow.
These solutions could help reverse decades of environmental damage. However, experts caution that releasing synthetic organisms into open ecosystems carries risks. Even well-intentioned organisms may mutate, spread, or interfere with existing species. While bioremediation could be one of synthetic biology’s greatest achievements, researchers insist it must be tested under strict safeguards before widespread use.
6. The Threat of Unintended Consequences

With any new technology, unintended outcomes are possible. Synthetic organisms may behave in ways scientists didn’t predict, creating ecological imbalances or health risks.
Some experts compare the challenge to invasive species, which often thrive in new environments at the expense of native ecosystems. Unlike natural invaders, however, synthetic lifeforms are designed by humans, making mistakes harder to undo. This is why scientists argue that every new organism should undergo rigorous testing and containment before being considered for release.
7. Biosecurity Concerns Around the World

Beyond accidents, synthetic biology also raises biosecurity worries. The tools used to create new organisms are becoming cheaper and more accessible, increasing the chance of misuse.
Experts fear that malicious actors could design harmful organisms intentionally, posing risks to global health and safety. To counter this, researchers and governments are urging strong international regulations. The challenge is finding a balance that supports scientific progress while ensuring synthetic biology does not become a weapon in the wrong hands.
8. Ethical Questions Scientists Can’t Ignore

Synthetic biology doesn’t only pose technical risks—it also raises ethical concerns. Should humans create entirely new forms of life, and who decides what limits should exist?
Critics warn that rushing ahead without thoughtful debate could lead to problems society isn’t prepared for. Supporters argue that ethical frameworks will help maximize benefits while minimizing risks. Either way, the discussion is now central to the field. Scientists agree that public trust will depend on how responsibly synthetic lifeforms are developed and managed.
9. The Push for Global Oversight

Because synthetic organisms could affect ecosystems worldwide, scientists say international cooperation is essential. No single nation can manage the risks alone.
Organizations like the National Academies of Sciences and the World Health Organization have called for global safeguards. These include transparency in research, shared safety standards, and early-warning systems. Without cooperation, uneven oversight could allow risky projects to move forward unchecked. Experts emphasize that preventing harm requires collaboration as much as innovation.
10. Balancing Benefits and Risks

Synthetic biology offers enormous potential benefits, from cleaner energy to better healthcare. At the same time, the risks—unintended or deliberate—cannot be ignored.
Scientists stress that the goal should not be to halt progress but to manage it wisely. Careful regulation, ethical oversight, and transparency could allow humanity to enjoy breakthroughs while reducing dangers. The future of synthetic lifeforms will depend on whether society can balance opportunity with responsibility.
11. What Comes Next for Synthetic Biology

The field of synthetic biology is moving fast, and the next decade will be critical. Advances could transform medicine, energy, and environmental protection on a global scale.
But experts warn that speed must not outpace caution. Strong safeguards, ethical frameworks, and international agreements are needed to guide progress. Synthetic lifeforms may hold the power to solve humanity’s greatest problems—or to create new ones. What happens next depends on how responsibly the world embraces this powerful technology.