Scientists are racing toward breakthroughs that could deliver limitless clean energy sooner than anyone imagined.
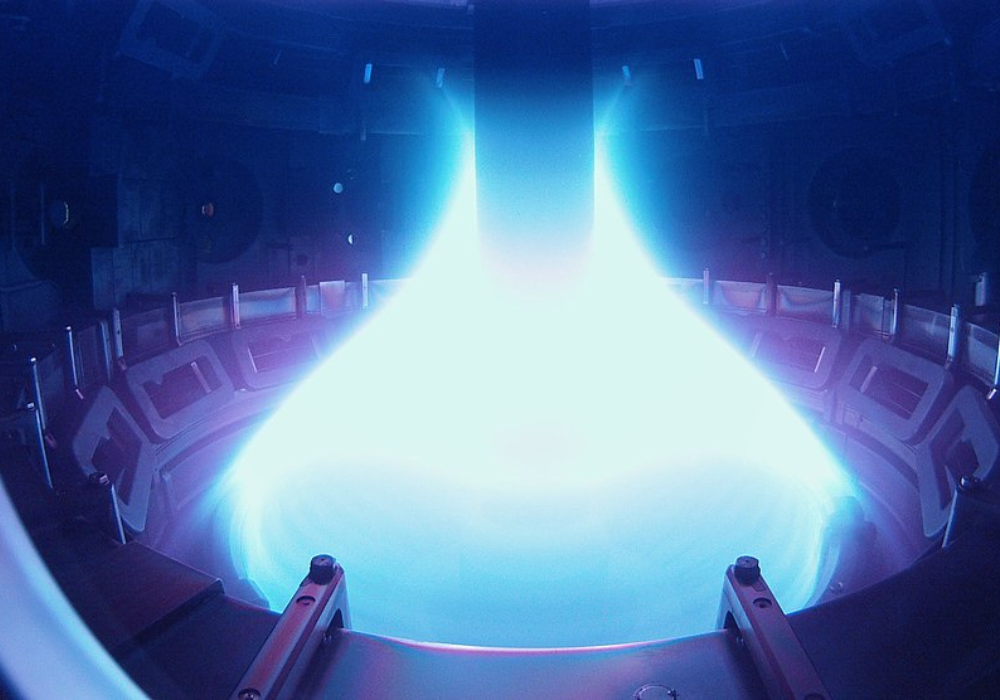
Nuclear fusion has long been described as the “holy grail” of energy—clean, safe, and virtually limitless. For decades, it felt like science fiction, always a distant dream. But now, researchers say the finish line is closer than ever.
In 2022, the U.S. Department of Energy confirmed that scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory achieved a net energy gain from fusion for the first time—a milestone once thought impossible. Experts caution there’s still work ahead, but the breakthrough shows fusion may arrive much faster than anyone expected, reshaping how the world powers its future.
1. Fusion is the power source of the stars

Nuclear fusion is the process that fuels the sun, where hydrogen atoms smash together under intense heat and pressure to release massive amounts of energy. Unlike fission, which splits atoms and creates long-lived radioactive waste, fusion produces energy by combining atoms.
The potential is staggering: just a small amount of hydrogen fuel could generate as much energy as tons of coal or oil. Harnessing the same reaction that powers the stars on Earth would provide virtually limitless clean energy.
2. A decades-long dream may finally be real
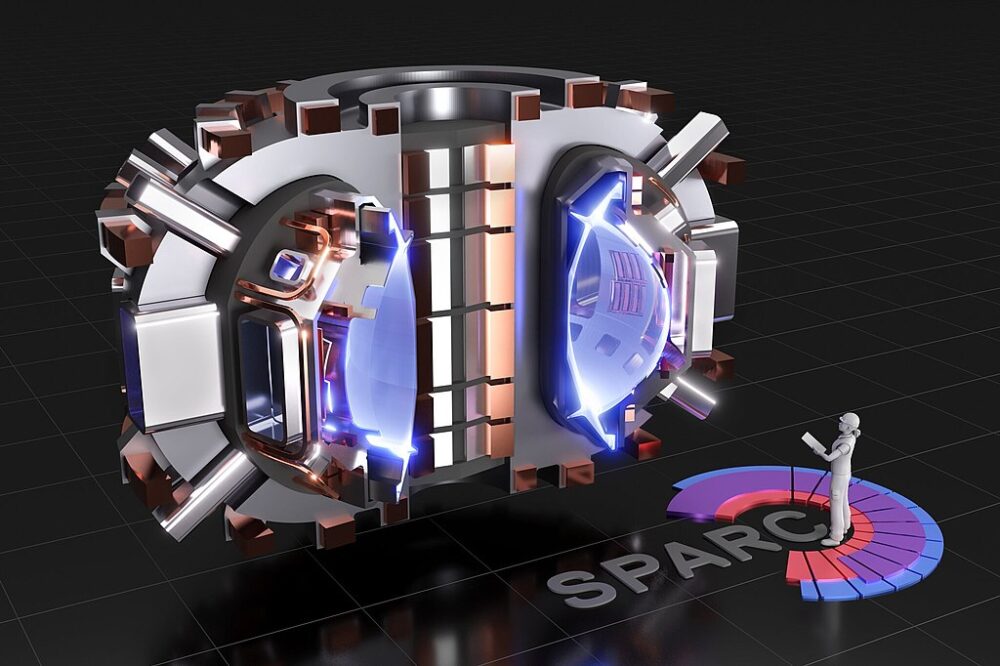
For more than half a century, scientists chased fusion only to see deadlines pushed further into the future. The running joke was that fusion was always “30 years away.”
That narrative is starting to change. Recent advances in laser technology, magnetic confinement, and computational modeling have brought scientists closer than ever. What was once a far-off fantasy is now on the brink of becoming a practical energy solution.
3. The breakthrough that changed everything
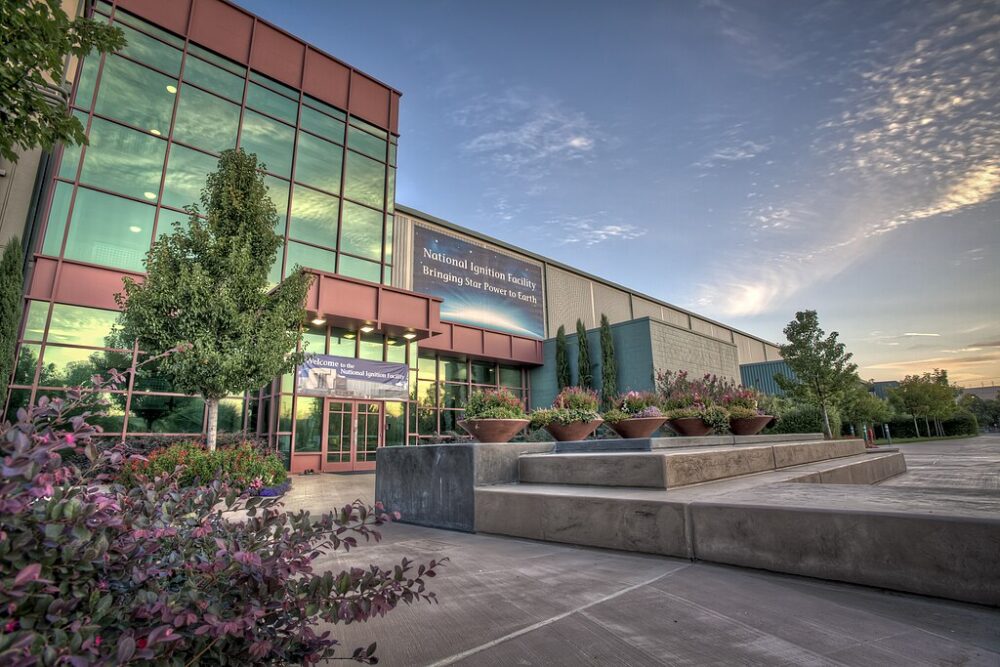

In December 2022, scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California achieved a world first: a fusion reaction that produced more energy than it consumed. Known as “ignition,” this was a milestone experts had sought for decades.
The U.S. Department of Energy hailed it as a historic breakthrough for science and energy. While scaling it to power grids will take time, the demonstration proved fusion energy isn’t just possible—it’s here.
4. Why fusion is so much cleaner than fission
Nuclear fission, used in today’s reactors, splits heavy atoms like uranium, leaving behind radioactive waste that lasts thousands of years. Fusion, by contrast, produces helium as its byproduct—the same harmless gas used in balloons.
Fusion also carries no risk of runaway meltdowns like Chernobyl or Fukushima. If something goes wrong, the reaction simply stops. This makes it one of the safest and cleanest energy sources humanity could ever deploy.
5. Magnetic fields are unlocking new possibilities

One approach to fusion involves giant magnets that trap plasma—the superheated state of matter where fusion occurs—inside doughnut-shaped chambers called tokamaks.
Recent breakthroughs in superconducting magnets have allowed scientists to sustain plasma longer and at higher energies. Projects like ITER in France and SPARC in the U.S. are betting that magnetic confinement will be the key to scaling fusion into real-world power plants.
6. Lasers are rewriting the fusion playbook

Another path, called inertial confinement, uses powerful lasers to compress tiny pellets of hydrogen fuel until they ignite. This was the approach that made headlines at Lawrence Livermore.
The world’s most powerful lasers now deliver bursts of energy so intense they can briefly replicate conditions inside the sun. Each success in this field brings scientists closer to turning these laboratory feats into practical energy production.
7. Private companies are racing ahead
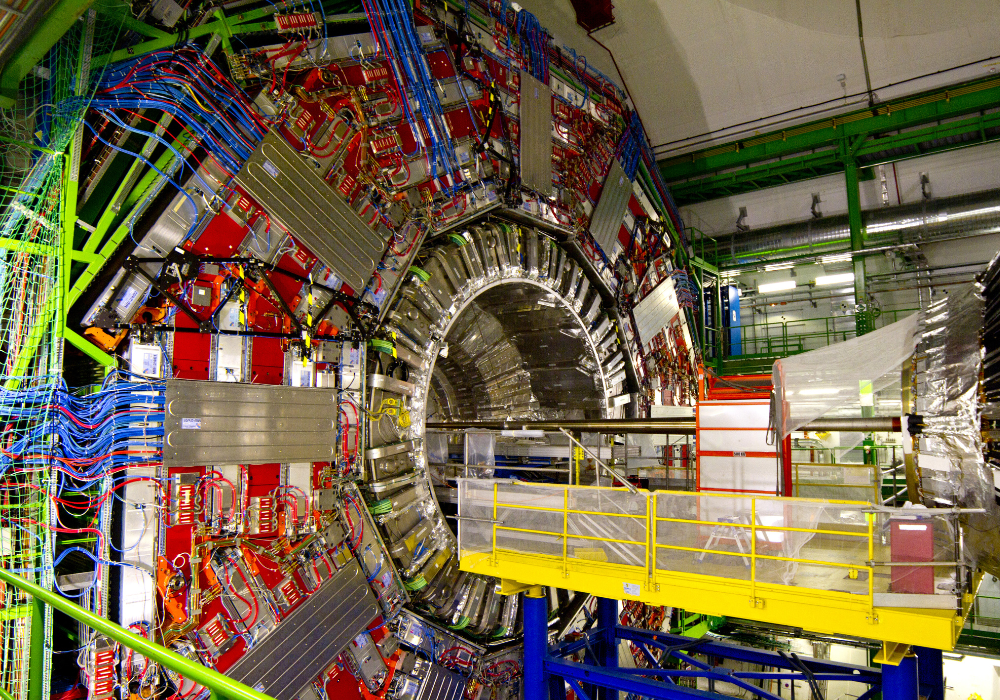
Fusion research was once the domain of governments and large international labs, but startups are now entering the race. Companies like Commonwealth Fusion Systems, TAE Technologies, and Helion are drawing billions in investment.
These firms promise smaller, cheaper, and faster designs compared to sprawling government projects. Investors see fusion not as a far-off gamble, but as a potentially revolutionary energy industry taking shape within our lifetimes.
8. The fuel is abundant and nearly limitless

Fusion fuel comes from isotopes of hydrogen, such as deuterium and tritium. Deuterium can be extracted from seawater, while tritium can be bred from lithium, which is already widely used in batteries.
This means the planet has enough potential fusion fuel to last millions of years. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and polluting, fusion offers energy security for countless generations if scientists can master the process.
9. Fusion could end the energy crisis

Global demand for electricity is rising fast, especially as more countries transition to electric vehicles and digital infrastructure. Fossil fuels still dominate, but their costs—economic, environmental, and political—are mounting.
Fusion offers a path to virtually unlimited clean energy that could replace coal, gas, and oil. Experts say this would not only slash carbon emissions but also stabilize energy markets and reduce dependence on volatile fuel supplies.
10. Challenges remain before fusion powers homes

Despite breakthroughs, major hurdles still stand in the way. Fusion reactions currently last only seconds, and the equipment needed is massive and expensive. Scaling laboratory success to grid-level power plants is a daunting task.
Scientists are confident progress will continue, but they caution against expecting instant results. Even optimistic timelines suggest commercial fusion power is still at least a decade away.
11. Governments are betting big on fusion

Countries around the world are investing heavily in fusion research. The European Union, China, Japan, and the U.S. have poured billions into projects aimed at making fusion practical.
The international ITER project in France is one of the largest scientific collaborations in history, designed to demonstrate large-scale fusion in the coming years. Governments see fusion not just as a scientific challenge, but as a key to energy independence.
12. The future of energy could be fusion-powered

Experts believe the world may one day look back on the 2020s as the decade fusion turned from dream to reality. If breakthroughs continue, fusion could power cities, industries, and transportation with virtually no pollution.
The implications are profound: a future where energy scarcity, carbon emissions, and dependence on fossil fuels are replaced by a safe, abundant power source drawn from the most basic element in the universe. For the first time, that future feels within reach.
