Nuclear power offers a reliable, low-carbon energy source crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.

Nuclear power stands out as a significant contributor in the fight against climate change by providing consistent, low-carbon electricity. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear reactors generate large amounts of energy without emitting greenhouse gases during operation, supporting a stable energy supply alongside renewables. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), incorporating nuclear energy is vital for achieving deep decarbonization goals while addressing challenges like waste management and safety advancements.
1. Nuclear power produces large amounts of reliable, low-carbon electricity consistently.
Nuclear power plants generate substantial amounts of low-carbon electricity steadily, making them vital in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Using uranium fuel, nuclear reactors convert atomic energy into electricity with a capacity that minimizes atmospheric carbon release, maintaining a consistent energy output.
This reliable energy production contrasts with intermittent sources like wind or solar. Nuclear facilities can provide a stable supply of power, supporting national grids day and night. Thus, they serve as a backbone for energy systems seeking to mitigate climate impacts by replacing fossil fuels with cleaner alternatives.
2. It generates energy without emitting greenhouse gases during operation.

Operating without emitting greenhouse gases, nuclear power produces energy through nuclear fission. The process involves splitting uranium atoms, releasing heat to produce steam that drives turbines, creating electricity. This mechanism bypasses burning fossil fuels, which typically release carbon dioxide.
While the fission process itself is clean, lifecycle emissions from constructing plants and fuel processing must be considered. However, these emissions are minimal compared to fossil fuel-powered plants. As such, nuclear energy remains a pivotal player in clean energy strategies, delivering significant reductions in overall carbon footprints.
3. Nuclear plants have high capacity factors, ensuring steady power supply.

Nuclear power plants have high capacity factors, often exceeding 90%, which means they produce electricity at maximum output continuously. This reliability ensures a constant energy supply. By contrast, certain renewable sources, like solar and wind, can be more intermittent due to weather fluctuations.
A stable capacity factor allows nuclear plants to meet baseline energy demands efficiently. This advantage makes nuclear energy essential for maintaining grid stability, especially when integrating variable renewables into national energy portfolios. Consequently, it strengthens energy systems by smoothing out supply variability, aiding large-scale energy transitions.
4. It can complement renewable energy sources by providing reliable baseload power.

Providing reliable baseload power, nuclear energy complements intermittent renewables like wind and solar. While renewables excel in reducing emissions, they depend on environmental conditions, necessitating dependable backup sources. Nuclear plants can supply this steady, round-the-clock power, balancing fluctuating renewable outputs.
By integrating nuclear with renewables, energy grids can achieve a more sustainable mix. This approach allows for maximizing emission reductions while maintaining electricity reliability. As a result, nuclear energy acts as a stabilizing force, facilitating the transition toward a carbon-light future in harmony with renewable technologies.
5. Advancements in reactor technology increase safety and efficiency.
Recent advancements in reactor technology have significantly enhanced nuclear safety and efficiency. Modern designs like Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and Generation IV reactors incorporate passive safety systems, reducing risks of overheating or core damage. These innovations reflect a shift towards safer operational practices.
Additionally, heightened efficiency reduces fuel usage and waste production. The technological strides in reactor design indicate a forward-thinking approach, addressing historical concerns while paving the way for broader acceptance. Thus, advances have improved public perception and potential deployment across global energy agendas.
6. Nuclear energy helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels and coal power.

Nuclear energy offers a compelling alternative to fossil fuels and coal, bolstering efforts to decarbonize electricity generation. By using nuclear reactors, countries can significantly cut their reliance on carbon-intensive energy sources. The transition reduces atmospheric carbon emissions, combating climate change effectively.
As a thermal energy source, nuclear can replace aging coal plants, supporting cleaner grids. This replacement aids in lowering associated health risks from air pollution. Expanding nuclear capacity is an essential component in transforming energy systems, contributing to overall emission reduction strategies and sustainable energy goals.
7. It requires relatively small land areas compared to some renewable sources.

Requiring relatively small land areas, nuclear facilities pack immense power production within compact footprints. In contrast, extensive land is often needed for solar farms or wind turbines, highlighting nuclear’s spatial efficiency. This characteristic makes it particularly advantageous in regions with limited available space.
Efficiency in land use can benefit countries seeking to enhance energy generation without sprawling into valuable land. By combining high density with low emissions, nuclear power offers a pragmatic solution for achieving energy security. In particular, urbanized areas can capitalize on this compact energy model.
8. Nuclear power supports economic growth through skilled jobs and industry expansion.

Economic growth finds a partner in nuclear power through skilled job creation and industry advancement. Building, maintaining, and operating nuclear plants require specialized expertise, fostering high-paying employment opportunities across engineering, construction, and technological research domains.
Moreover, nuclear innovation catalyzes industrial expansion, enhancing local economies. From training programs to long-term careers, nuclear power sustains economic vitality while contributing to a sustainable future. As countries invest in nuclear infrastructure, the ripple effects extend beyond energy, underpinning broader economic development goals with sustained growth potential.
9. The fuel supply for nuclear reactors is abundant and widely available.

Nuclear reactors rely on a fuel supply that’s both abundant and widely available. Uranium, the primary fuel, is found in various geological formations globally, ensuring a steady, long-term energy source. This availability bolsters the security of nuclear-based electricity generation.
Additionally, advanced reactors can utilize alternative fuels like thorium, further diversifying the fuel landscape. With secure reserves and technological adaptability, nuclear energy can confidently support energy independence. This stability contributes to uninterrupted power availability, steering nations away from the volatility associated with fossil fuel markets.
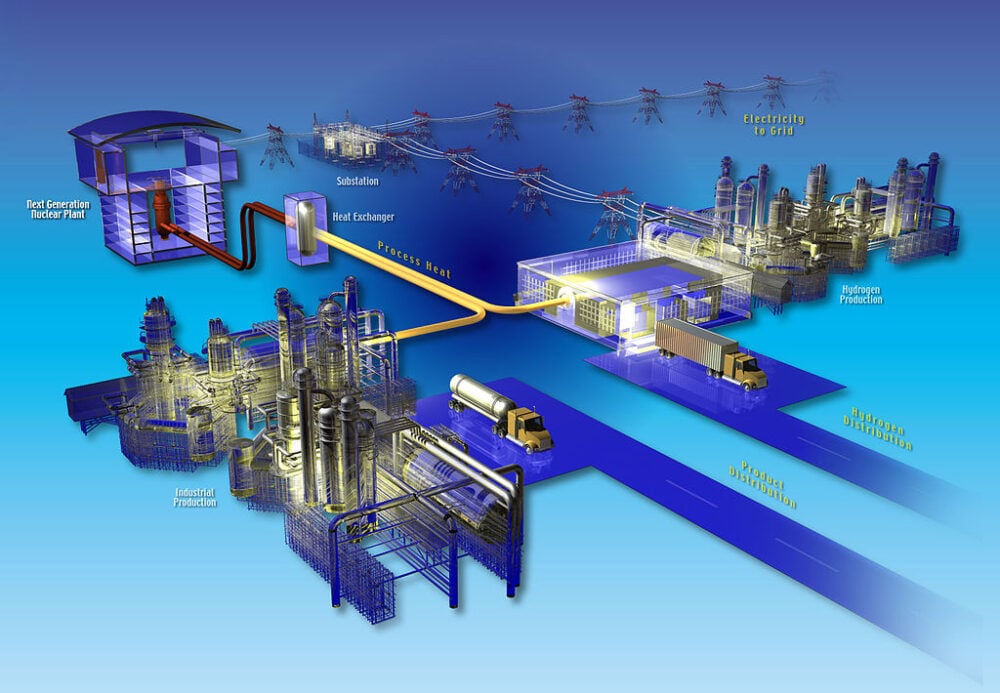
10. Nuclear technology can contribute to hydrogen production with low emissions.
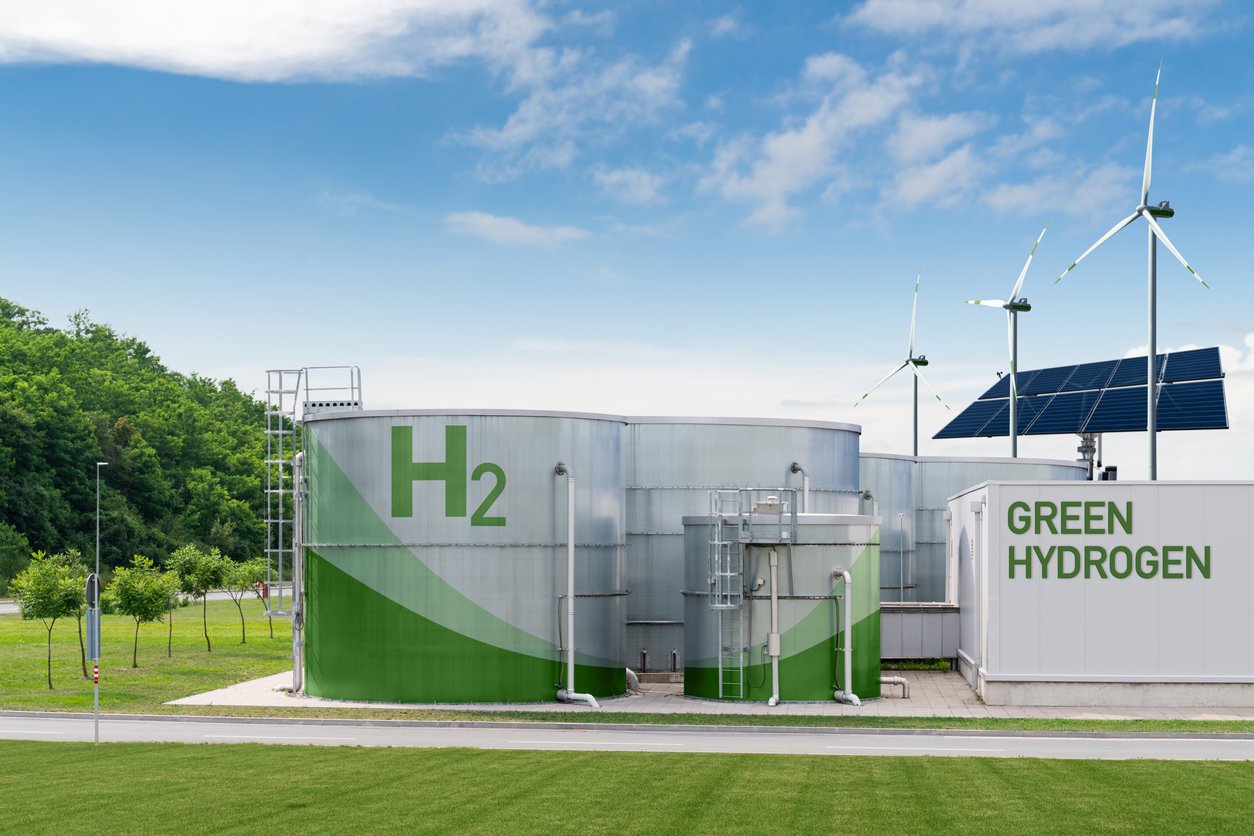

The link between nuclear technology and hydrogen production opens pathways for low-emission alternatives in various sectors. High-temperature reactors can produce hydrogen with minimal carbon output, offering cleaner options than traditional natural gas methods.
This capability supports decarbonization efforts in transportation and industry, aligning with global emissions targets. By leveraging nuclear hydrogen production, heavy industries can pivot towards greener practices, including steel manufacturing and chemical production. Thus, nuclear technology extends its influence beyond electricity, fostering broader low-carbon opportunities within diverse economic structures.
11. It offers potential for carbon-free energy in heavy industries and transport.

Offering carbon-free energy potential in heavy industries and transport, nuclear power supports emissions reduction beyond electrification. High-temperature nuclear reactors can produce heat necessary for industrial processes like steel or cement production without releasing carbon emissions.
As industries explore alternatives to fossil fuels, nuclear technology provides a viable solution for decarbonization. Energy-intensive transportation modes, such as ships or trains, might also benefit from nuclear’s low-emission capacity. By addressing energy needs holistically, nuclear power becomes a versatile tool driving comprehensive climate-conscious industrial transformations.
12. Newer reactor designs produce less waste and improve resource utilization.

Newer reactor designs focus on minimizing waste, illustrating a commitment to improved resource utilization. Technologies like small modular reactors and thorium reactors generate less radioactive waste, enhancing sustainability in nuclear power cycles.
By optimizing fuel use, these advancements extend the operational life of reactors, promoting efficiency. As nuclear sustainability improves, waste management becomes more manageable. This progress underlines a shift towards responsible development, aiming for a comprehensive balance between energy production and environmental stewardship within the nuclear landscape.
