Extreme weather keeps testing a system experts say is dangerously outdated.

Storms reveal critical weak points in power grid infrastructure that can lead to widespread outages. From aging transformers to poor vegetation management, these vulnerabilities highlight the need for improved design and maintenance. Understanding these common failure points helps utilities and communities prepare for storm-related disruptions and invest in resilience measures. Expert insights from IEEE, NIST, and the US Department of Energy emphasize the importance of addressing these issues to maintain stable power delivery.
1. Overhead power lines are vulnerable to strong winds and falling trees.
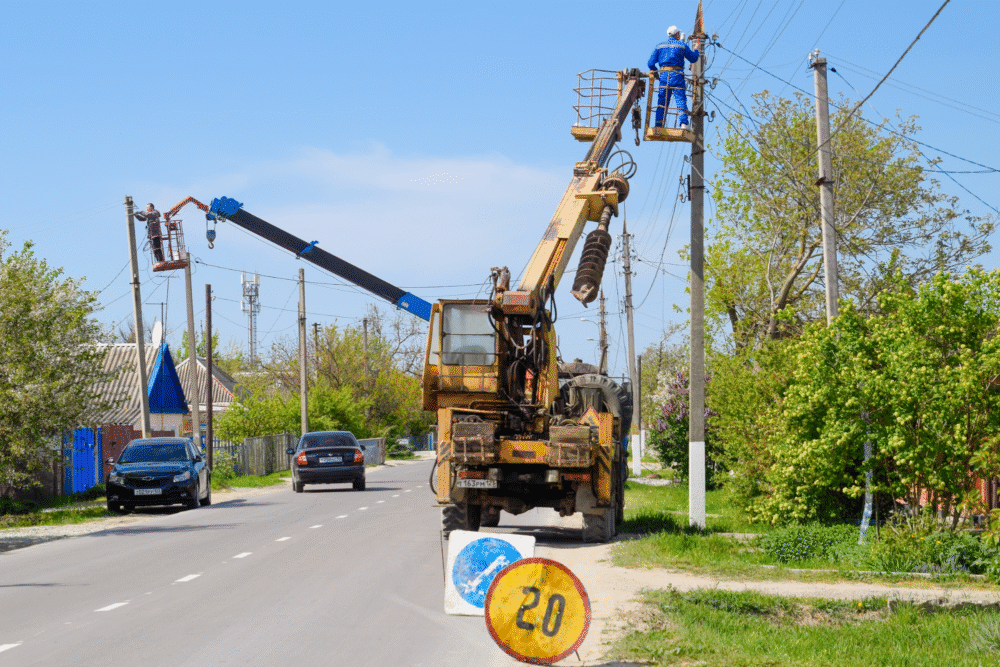

Overhead power lines, crucial for distributing electricity, are particularly susceptible to damage from strong winds and falling trees during storms. Their elevated position means they can sway or break when subjected to severe weather, leading to potential widespread power outages.
Such vulnerabilities highlight the need for more robust design and enhanced maintenance to withstand extreme conditions. Proactive management, including regular trimming of nearby vegetation and improved structural supports, can reduce the likelihood of these failures, providing communities with greater continuity of electrical service during adverse weather events.
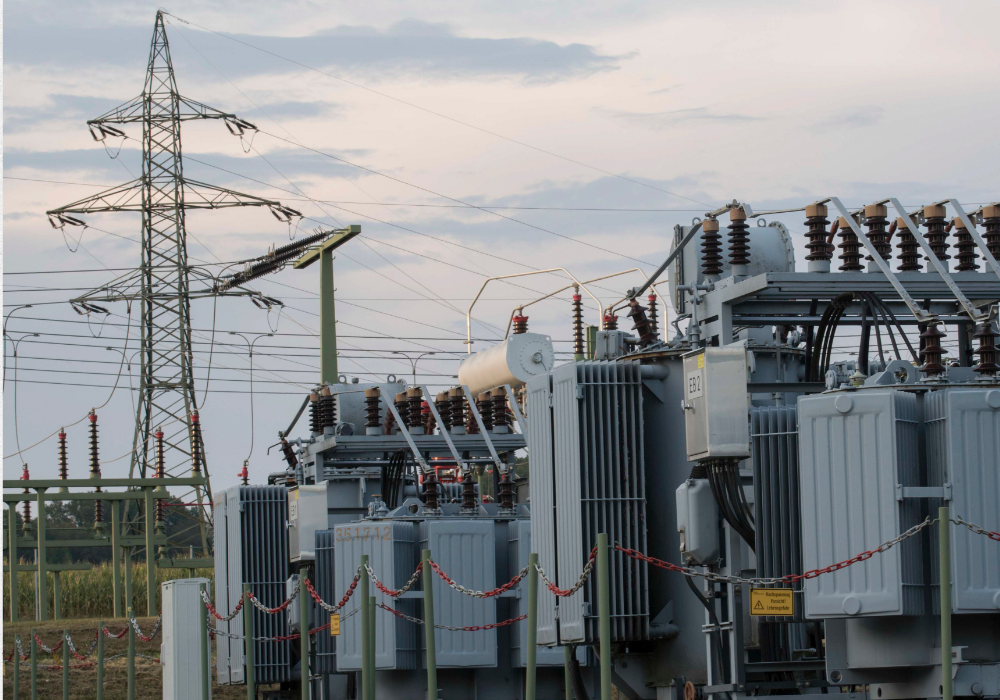
2. Aging transformers prone to failure during electrical surges.

Transformers, often seen atop utility poles or within substations, are vital for voltage regulation but can age over time, making them prone to failure. During electrical surges often associated with storms, these aging components may malfunction or completely fail.
The potential for such failures underscores the importance of upgrading and replacing old transformers to enhance grid reliability. By prioritizing technological advancements and regular inspections, electric utilities can mitigate the risk of widespread damage and lengthy outages, ensuring more stable power delivery even during stormy weather.
3. Underground cables at risk from flooding and soil erosion.
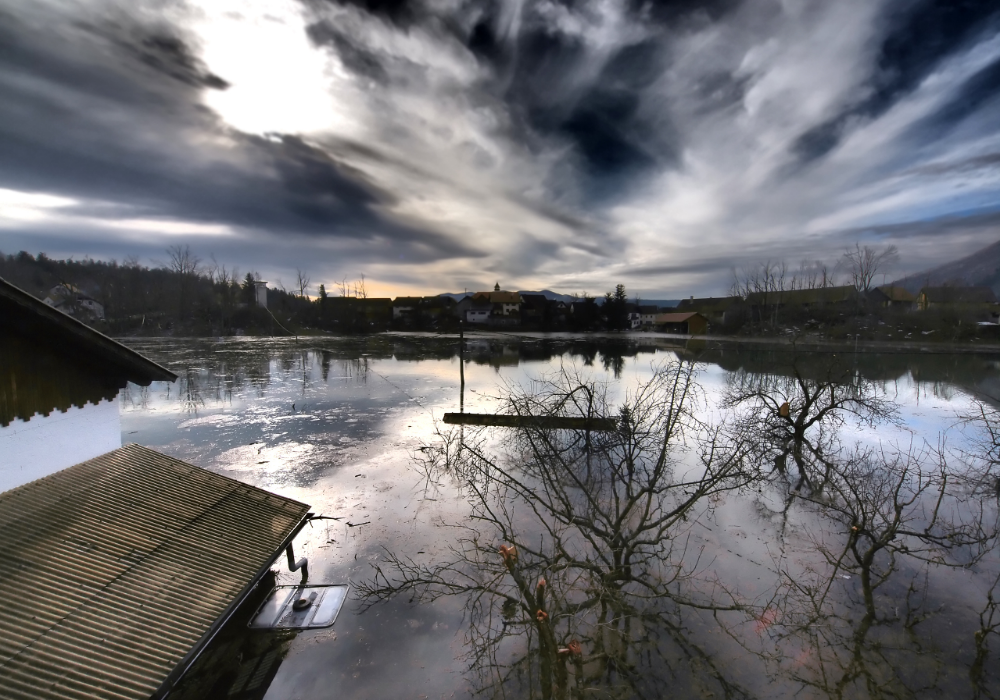

Underground cables, though generally protected from direct wind and tree damage, face significant risks from flooding and soil erosion. When water or shifting ground penetrates their protective barriers, it can lead to severe cable damage and subsequent power disruptions.
The challenges faced by these cables highlight the need for improved waterproofing technologies and better drainage systems to protect infrastructure. Strengthening these underground assets can help ensure continued power delivery, even during periods of heavy rain or flooding, enhancing overall grid reliability.
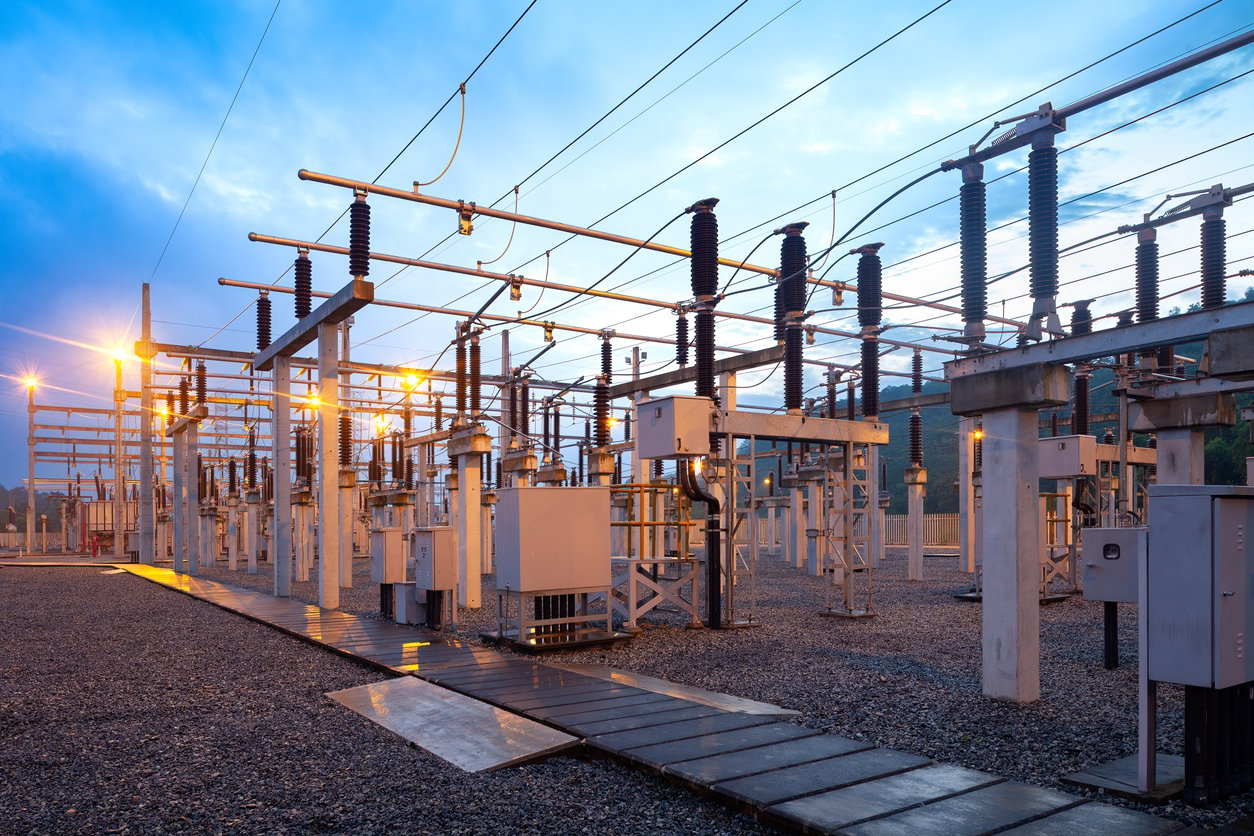
4. Substation equipment exposed to water damage and overheating.
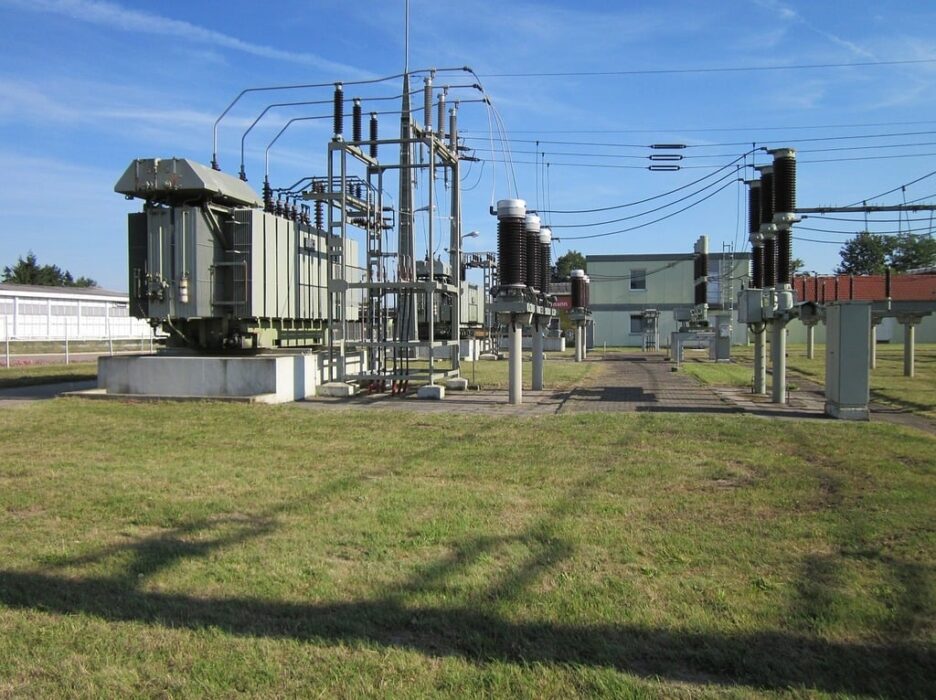

Substation equipment is at risk from environmental factors, particularly water damage and overheating, which are common during storms. Exposure to excessive moisture can lead to rust, corrosion, and equipment failures, compromising power grid stability.
Implementing robust weatherproofing measures and installing cooling systems can mitigate these hazards. Ensuring that the critical components of substations remain operational during adverse conditions is crucial for maintaining consistent electricity flow, minimizing outages, and reducing repair costs over time.
5. Insufficient insulation increases risk of short circuits in storms.

Inadequate insulation on electrical components can increase the risk of short circuits, especially during storms when moisture levels rise. Without sufficient protection, water ingress can cause electric arcs leading to equipment failures and widespread outages.
Understanding this vulnerability emphasizes the importance of using high-quality insulators and sealing techniques. By improving insulation materials and maintaining existing installations, the power grid can be safeguarded against storm-induced failures, ensuring greater electrical reliability for end-users.
6. Weak connection points that may loosen under heavy vibrations.
Weak connection points in power grid infrastructures, such as connectors and joints, may loosen due to heavy vibrations caused by strong winds or equipment operation. These weakened points can result in interruptions or unstable power supply during severe weather events.
Addressing these points of vulnerability through regular inspection and tightening processes helps maintain electrical service integrity. By ensuring robust connections, utility providers can fortify the grid against adverse conditions, reducing the likelihood of downtime and service interruptions.
7. Outdated circuit breakers failing to interrupt fault currents effectively.
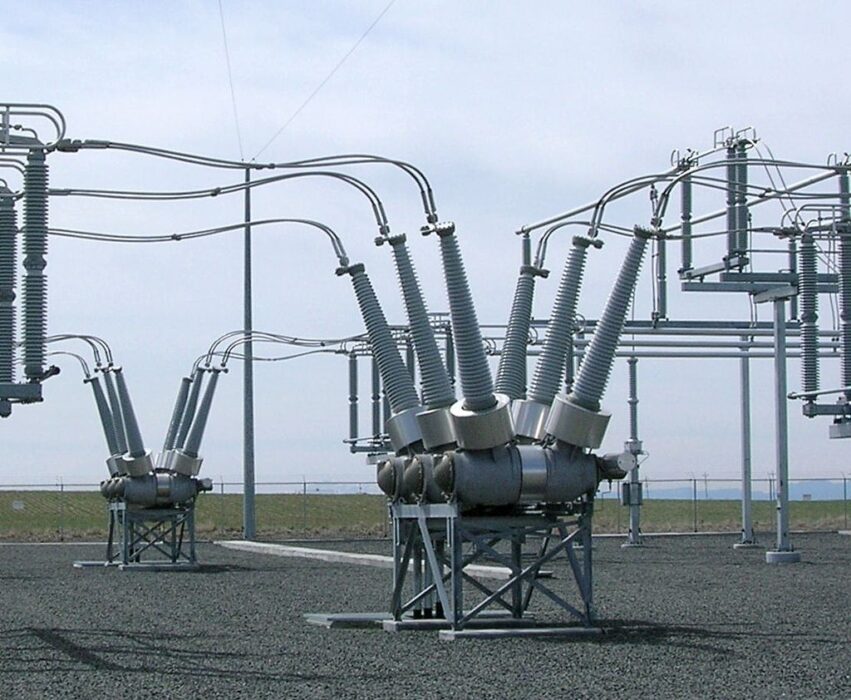

Outdated circuit breakers in power grids may fail to handle fault currents effectively, especially under severe electrical stress during storms. This failure can exacerbate outages as breakers are meant to prevent damage by interrupting circuits in fault conditions.
To enhance system resilience, upgrading these breakers to modern standards is essential. Newer models with advanced fault detection capabilities and faster response times ensure rapid resolution of issues. Upgrading these components is a critical step in reducing grid vulnerabilities and maintaining power continuity.
8. Lack of redundancy creating single points of failure in grids.

Power grids often suffer from a lack of redundancy, which creates single points of failure that can lead to extensive outages when a component fails. Without alternative pathways for electricity, a failure in one part can disrupt the entire system.
Building redundancy into grid infrastructure ensures there are backup systems in place to pick up the slack if a primary system fails. By investing in this approach, electric utilities can better withstand component failures and reduce the impact of localized disruptions, thus maintaining stable power supply.
9. Poor vegetation management leading to frequent line interruptions.

Poor vegetation management around power lines often results in branches contacting lines during storms, causing frequent interruptions. Overhanging trees can fall or break onto lines, leading to power cuts and equipment damage.
Efficient vegetation management, through regular trimming and clearing of potential hazards, can prevent these incidents. Clearing vegetation not only reduces the risk of contact but also minimizes potential fire dangers, helping to ensure uninterrupted power delivery during severe weather.
10. Inadequate lightning protection systems causing extensive outages.

Inadequate lightning protection systems leave power grids vulnerable to extensive outages during thunderstorms. Without effective grounding and surge protection, lightning strikes can cause significant damage to infrastructure, leading to widespread power loss.
Implementing comprehensive lightning protection measures, such as advanced grounding techniques and surge arresters, can reduce these risks. Enhancing these systems improves the durability and resilience of the grid, ensuring it can withstand and quickly recover from storm-related impacts.